VEGFB/VEGFR1-Induced Expansion of Adipose Vasculature Counteracts Obesity and Related Metabolic Complications
- PMID: 27076080
- PMCID: PMC5898626
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.03.004
VEGFB/VEGFR1-Induced Expansion of Adipose Vasculature Counteracts Obesity and Related Metabolic Complications
Abstract
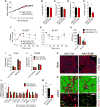
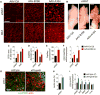
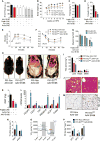
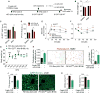
Impaired angiogenesis has been implicated in adipose tissue dysfunction and the development of obesity and associated metabolic disorders. Here, we report the unexpected finding that vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGFB) gene transduction into mice inhibits obesity-associated inflammation and improves metabolic health without changes in body weight or ectopic lipid deposition. Mechanistically, the binding of VEGFB to VEGF receptor 1 (VEGFR1, also known as Flt1) activated the VEGF/VEGFR2 pathway and increased capillary density, tissue perfusion, and insulin supply, signaling, and function in adipose tissue. Furthermore, endothelial Flt1 gene deletion enhanced the effect of VEGFB, activating the thermogenic program in subcutaneous adipose tissue, which increased the basal metabolic rate, thus preventing diet-induced obesity and related metabolic complications. In obese and insulin-resistant mice, Vegfb gene transfer, together with endothelial Flt1 gene deletion, induced weight loss and mitigated the metabolic complications, demonstrating the therapeutic potential of the VEGFB/VEGFR1 pathway.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
VEGF-B Improves Metabolic Health through Vascular Pruning of Fat.Cell Metab. 2016 Apr 12;23(4):571-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.03.012. Cell Metab. 2016. PMID: 27076071
References
-
- Aase K, von Euler G, Li X, Ponten A, Thorén P, Cao R, Cao Y, Olofsson B, Gebre-Medhin S, Pekny M, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-B-deficient mice display an atrial conduction defect. Circulation. 2001;104:358–364. - PubMed
-
- Anisimov A, Leppänen VM, Tvorogov D, Zarkada G, Jeltsch M, Holopainen T, Kaijalainen S, Alitalo K. The basis for the distinct biological activities of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 ligands. Sci Signal. 2013;6:ra52. - PubMed
-
- Ayala JE, Bracy DP, McGuinness OP, Wasserman DH. Considerations in the design of hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps in the conscious mouse. Diabetes. 2006;55:390–397. - PubMed
-
- Baba T, Shimada K, Neugebauer S, Yamada D, Hashimoto S, Watanabe T. The oral insulin sensitizer, thiazolidinedione, increases plasma vascular endothelial growth factor in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:953–954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

