Oncogenic Wnt3a expression as an estimable prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27076768
- PMCID: PMC4814746
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3829
Oncogenic Wnt3a expression as an estimable prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To investigate member 3a of Wingless-type MMTV integration site family (Wnt3a) expression in cancerous and surrounding tissues and the relationship between clinicopathologic features of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and Wnt3a expression.
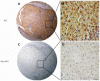
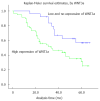
Methods: Wnt3a expression and cellular distribution and clinicopathologic characteristics in cancerous tissue and matched surrounding tissues were analyzed in 80 HCC patients from January 2006 to August 2008 by tissue microarrays and immunohistochemistry. The overall and disease-free survival rates were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and compared with the log-rank test. The prognostic analysis was carried out with univariate and multivariate Cox regressions models.
Results: The incidence of oncogenic Wnt3a expression in the cancerous group was up to 96.25% (77 of 80), which was significantly higher (χ(2) = 48.818, P < 0.001) than that in the surrounding group (46.25%, 37 of 80). Brown Wnt3a staining gradually increased with clinical staging that showed very strong staining in advanced HCC. The clinicopathologic features of high Wnt3a expression in HCC were related to poorly-differentiated grade (χ(2) = 20.211, P < 0.001), liver cirrhosis (χ(2) = 8.467, P < 0.004), hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection (χ(2) = 12.957, P < 0.001), higher tumor-node-metastasis stage (χ(2) = 22.960, P < 0.001), and 5-year survival rate (χ(2) = 15.469, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Oncogenic Wnt3a expression associated with HBV infection and cirrhotic liver might be an independent prognostic factor for HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Immunohistochemistry; Prognosis; Tissue microarrays; Wnt/β-catenin signal; Wnt3a.
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Ringelhan M, O’Connor T, Protzer U, Heikenwalder M. The direct and indirect roles of HBV in liver cancer: prospective markers for HCC screening and potential therapeutic targets. J Pathol. 2015;235:355–367. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1118–1127. - PubMed
-
- Maluccio M, Covey A. Recent progress in understanding, diagnosing, and treating hepatocellular carcinoma. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:394–399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

