Contribution of elevated intracellular calcium to pulmonary arterial myocyte alkalinization during chronic hypoxia
- PMID: 27076907
- PMCID: PMC4809666
- DOI: 10.1086/685053
Contribution of elevated intracellular calcium to pulmonary arterial myocyte alkalinization during chronic hypoxia
Abstract
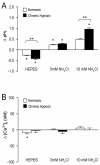
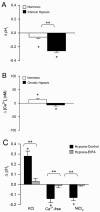
In the lung, exposure to chronic hypoxia (CH) causes pulmonary hypertension, a debilitating disease. Development of this condition arises from increased muscularity and contraction of pulmonary vessels, associated with increases in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell (PASMC) intracellular pH (pHi) and Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)]i). In this study, we explored the interaction between pHi and [Ca(2+)]i in PASMCs from rats exposed to normoxia or CH (3 weeks, 10% O2). PASMC pHi and [Ca(2+)]i were measured with fluorescent microscopy and the dyes BCECF and Fura-2. Both pHi and [Ca(2+)]i levels were elevated in PASMCs from hypoxic rats. Exposure to KCl increased [Ca(2+)]i and pHi to a similar extent in normoxic and hypoxic PASMCs. Conversely, removal of extracellular Ca(2+) or blockade of Ca(2+) entry with NiCl2 or SKF 96365 decreased [Ca(2+)]i and pHi only in hypoxic cells. Neither increasing pHi with NH4Cl nor decreasing pHi by removal of bicarbonate impacted PASMC [Ca(2+)]i. We also examined the roles of Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange (NCX) and Na(+)/H(+) exchange (NHE) in mediating the elevated basal [Ca(2+)]i and Ca(2+)-dependent changes in PASMC pHi. Bepridil, dichlorobenzamil, and KB-R7943, which are NCX inhibitors, decreased resting [Ca(2+)]i and pHi only in hypoxic PASMCs and blocked the changes in pHi induced by altering [Ca(2+)]i. Exposure to ethyl isopropyl amiloride, an NHE inhibitor, decreased resting pHi and prevented changes in pHi due to changing [Ca(2+)]i. Our findings indicate that, during CH, the elevation in basal [Ca(2+)]i may contribute to the alkaline shift in pHi in PASMCs, likely via mechanisms involving reverse-mode NCX and NHE.
Keywords: Na+/Ca2+exchange; Na+/H+ exchange; hypoxic pulmonary hypertension.
Figures




References
-
- Rios EJ, Fallon M, Wang J, Shimoda LA. Chronic hypoxia elevates intracellular pH and activates Na+/H+ exchange in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2005;289(5):L867–L874. - PubMed
-
- Shimoda LA, Fallon M, Pisarcik S, Wang J, Semenza GL. HIF-1 regulates hypoxic induction of NHE1 expression and alkalinization of intracellular pH in pulmonary arterial myocytes. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2006;291(5):L941–L99. - PubMed
-
- Quinn DA, Honeyman TW, Joseph PM, Thompson BT, Hales CA, Scheid CR. Contribution of Na+/H+ exchange to pH regulation in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1991;5(6):586–591. - PubMed
-
- Quinn DA, Dahlberg CG, Bonventre JP, Scheid CR, Honeyman T, Joseph PM, Thompson BT, Hales CA. The role of Na+/H+ exchange and growth factors in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1996;14(2):139–145. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

