Proximity assays for sensitive quantification of proteins
- PMID: 27077033
- PMCID: PMC4822221
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bdq.2015.04.002
Proximity assays for sensitive quantification of proteins
Abstract
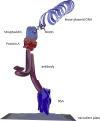
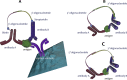
Proximity assays are immunohistochemical tools that utilise two or more DNA-tagged aptamers or antibodies binding in close proximity to the same protein or protein complex. Amplification by PCR or isothermal methods and hybridisation of a labelled probe to its DNA target generates a signal that enables sensitive and robust detection of proteins, protein modifications or protein-protein interactions. Assays can be carried out in homogeneous or solid phase formats and in situ assays can visualise single protein molecules or complexes with high spatial accuracy. These properties highlight the potential of proximity assays in research, diagnostic, pharmacological and many other applications that require sensitive, specific and accurate assessments of protein expression.
Keywords: Immuno-PCR; Immunoassays; In situ assays; Proximity extension assay; Proximity ligation assay.
Figures
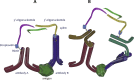

Similar articles
-
Homogeneous and digital proximity ligation assays for the detection of Clostridium difficile toxins A and B.Biomol Detect Quantif. 2016 Aug 31;10:2-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bdq.2016.06.003. eCollection 2016 Dec. Biomol Detect Quantif. 2016. PMID: 27990343 Free PMC article.
-
[In situ proximity ligation assay for detection of proteins, their interactions and modifications].Klin Onkol. 2014;27 Suppl 1:S87-91. doi: 10.14735/amko20141s87. Klin Onkol. 2014. PMID: 24945543 Czech.
-
Parallel protein detection by solid-phase proximity ligation assay with real-time PCR or sequencing.Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2015 Jan 5;109:20.10.1-20.10.25. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb2010s109. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25559104
-
Proximity ligation assay: an ultrasensitive method for protein quantification and its applications in pathogen detection.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Feb;105(3):923-935. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-11049-1. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33427935 Review.
-
Recent progress in developing proximity ligation assays for pathogen detection.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015;15(7):861-7. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2015.1044440. Epub 2015 May 8. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015. PMID: 25955213 Review.
Cited by
-
Improving Quality, Reproducibility, and Usability of FRET-Based Tension Sensors.Cytometry A. 2019 Feb;95(2):201-213. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.23688. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Cytometry A. 2019. PMID: 30523675 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated levels of several chemokines in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage are associated with worse clinical outcome.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 9;18(3):e0282424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282424. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36893189 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review on current COVID-19 detection methods: From lab care to point of care diagnosis.Sens Int. 2021;2:100119. doi: 10.1016/j.sintl.2021.100119. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Sens Int. 2021. PMID: 34766062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assay methods based on proximity-enhanced reactions for detecting non-nucleic acid molecules.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jun 29;11:1188313. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1188313. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37456730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisomal fission is modulated by the mitochondrial Rho-GTPases, Miro1 and Miro2.EMBO Rep. 2020 Feb 5;21(2):e49865. doi: 10.15252/embr.201949865. Epub 2020 Jan 2. EMBO Rep. 2020. PMID: 31894645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bustin S.A. IUL Press; La Jolla, CA: 2004. A–Z of quantitative PCR.
-
- Higuchi R., Fockler C., Dollinger G., Watson R. Kinetic PCR analysis: real-time monitoring of DNA amplification reactions. Biotechnology (NY) 1993;11:1026–1030. - PubMed
-
- Gibson U.E., Heid C.A., Williams P.M. A novel method for real time quantitative RT-PCR. Genome Res. 1996;6:995–1001. - PubMed
-
- Heid C.A., Stevens J., Livak K.J., Williams P.M. Real time quantitative PCR. Genome Res. 1996;6:986–994. - PubMed
-
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971;8:871–874. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
