Cerebral Glioma Grading Using Bayesian Network with Features Extracted from Multiple Modalities of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- PMID: 27077923
- PMCID: PMC4831834
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153369
Cerebral Glioma Grading Using Bayesian Network with Features Extracted from Multiple Modalities of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Erratum in
-
Correction: Cerebral Glioma Grading Using Bayesian Network with Features Extracted from Multiple Modalities of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 2;11(6):e0157095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157095. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27254410 Free PMC article.
Abstract
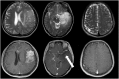
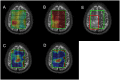
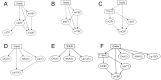
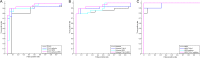
Many modalities of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have been confirmed to be of great diagnostic value in glioma grading. Contrast enhanced T1-weighted imaging allows the recognition of blood-brain barrier breakdown. Perfusion weighted imaging and MR spectroscopic imaging enable the quantitative measurement of perfusion parameters and metabolic alterations respectively. These modalities can potentially improve the grading process in glioma if combined properly. In this study, Bayesian Network, which is a powerful and flexible method for probabilistic analysis under uncertainty, is used to combine features extracted from contrast enhanced T1-weighted imaging, perfusion weighted imaging and MR spectroscopic imaging. The networks were constructed using K2 algorithm along with manual determination and distribution parameters learned using maximum likelihood estimation. The grading performance was evaluated in a leave-one-out analysis, achieving an overall grading accuracy of 92.86% and an area under the curve of 0.9577 in the receiver operating characteristic analysis given all available features observed in the total 56 patients. Results and discussions show that Bayesian Network is promising in combining features from multiple modalities of MRI for improved grading performance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Law M, Yang S, Wang H, Babb JS, Johnson G, Cha S, et al. Glioma grading: Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of perfusion MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopic imaging compared with conventional MR imaging. American Journal of Neuroradiology. 2003;24(10):1989–98. WOS:000186744800013. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

