Enzymatically Modified Low-Density Lipoprotein Promotes Foam Cell Formation in Smooth Muscle Cells via Macropinocytosis and Enhances Receptor-Mediated Uptake of Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein
- PMID: 27079883
- PMCID: PMC4882225
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307306
Enzymatically Modified Low-Density Lipoprotein Promotes Foam Cell Formation in Smooth Muscle Cells via Macropinocytosis and Enhances Receptor-Mediated Uptake of Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein
Abstract
Objective: Enzyme-modified nonoxidized low-density lipoprotein (ELDL) is present in human atherosclerotic lesions. Our objective is to understand the mechanisms of ELDL uptake and its effects on vascular smooth muscle cells (SMC).
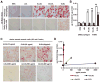
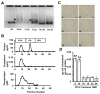
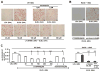
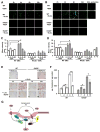
Approach and results: Transformation of murine aortic SMCs into foam cells in response to ELDL was analyzed. ELDL, but not acetylated or oxidized LDL, was potent in inducing SMC foam cell formation. Inhibitors of macropinocytosis (LY294002, wortmannin, amiloride) attenuated ELDL uptake. In contrast, inhibitors of receptor-mediated endocytosis (dynasore, sucrose) and inhibitor of caveolae-/lipid raft-mediated endocytosis (filipin) had no effect on ELDL uptake in SMC, suggesting that macropinocytosis is the main mechanism of ELDL uptake by SMC. Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is not obligatory for ELDL-induced SMC foam cell formation, but primes SMC for the uptake of oxidized LDL in a RAGE-dependent manner. ELDL increased intracellular reactive oxygen species, cytosolic calcium, and expression of lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1 in wild-type SMC but not in RAGE(-/-) SMC. The macropinocytotic uptake of ELDL is regulated predominantly by intracellular calcium because ELDL uptake was completely inhibited by pretreatment with the calcium channel inhibitor lacidipine in wild-type and RAGE(-/-) SMC. This is in contrast to pretreatment with PI3 kinase inhibitors which completely prevented ELDL uptake in RAGE(-/-) SMC, but only partially in wild-type SMC.
Conclusions: ELDL is highly potent in inducing foam cells in murine SMC. ELDL endocytosis is mediated by calcium-dependent macropinocytosis. Priming SMC with ELDL enhances the uptake of oxidized LDL.
Keywords: amiloride; atherosclerosis; endocytosis; foam cells; wortmannin.
© 2016 American Heart Association, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Nakashima Y, Wight TN, Sueishi K. Early atherosclerosis in humans: Role of diffuse intimal thickening and extracellular matrix proteoglycans. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;79:14–23. - PubMed
-
- Orekhov AN, Andreeva ER, Krushinsky AV, Novikov ID, Tertov VV, Nestaiko GV, Khashimov KA, Repin VS, Smirnov VN. Intimal cells and atherosclerosis. Relationship between the number of intimal cells and major manifestations of atherosclerosis in the human aorta. Am J Pathol. 1986;125:402–415. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bauriedel G, Hutter R, Welsch U, Bach R, Sievert H, Lüderitz B. Role of smooth muscle cell death in advanced coronary primary lesions: Implications for plaque instability. Cardiovasc Res. 1999;41:480–488. - PubMed
-
- Linton MF, Fazio S. Macrophages, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003;27(Suppl 3):S35–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

