Clinical impacts of genomic copy number gains at Xq28
- PMID: 27081496
- PMCID: PMC4785515
- DOI: 10.1038/hgv.2014.1
Clinical impacts of genomic copy number gains at Xq28
Abstract
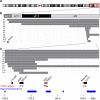
Duplications of the Xq28 region are the most frequent chromosomal aberrations observed in patients with intellectual disability (ID), especially in males. These duplications occur by variable mechanisms, including interstitial duplications mediated by segmental duplications in this region and terminal duplications (functional disomy) derived from translocation with other chromosomes. The most commonly duplicated region includes methyl CpG-binding protein 2 gene (MECP2), which has a minimal duplicated size of 0.2 Mb. Patients with MECP2 duplications show severe ID, intractable seizures and recurrent infections. Duplications in the telomeric neighboring regions, which include GDP dissociation inhibitor 1 gene (GDI1) and ras-associated protein RAB39B gene (RAB39B), are independently associated with ID, and many segmental duplications located in this region could mediate these frequently observed interstitial duplications. In addition, large duplications, including MECP2 and GDI1, induce hypoplasia of the corpus callosum. Abnormalities observed in the white matter, revealed by brain magnetic resonance imaging, are a common finding in patients with MECP2 duplications. As primary sequence analysis cannot be used to determine the region responsible for chromosomal duplication syndrome, finding this region relies on the collection of genotype-phenotype data from patients.
Figures

References
-
- Froyen G, Van Esch H, Bauters M, Hollanders K, Frints SG, Vermeesch JR et al. Detection of genomic copy number changes in patients with idiopathic mental retardation by high-resolution X-array-CGH: important role for increased gene dosage of XLMR genes. Hum Mutat 2007; 28: 1034–1042. - PubMed
-
- Najm J, Horn D, Wimplinger I, Golden JA, Chizhikov VV, Sudi J et al. Mutations of CASK cause an X-linked brain malformation phenotype with microcephaly and hypoplasia of the brainstem and cerebellum. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1065–1067. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi S, Okamoto N, Chinen Y, Takanashi J, Makita Y, Hata A et al. Novel intragenic duplications and mutations of CASK in patients with mental retardation and microcephaly with pontine and cerebellar hypoplasia (MICPCH). Hum Genet 2012; 131: 99–110. - PubMed
-
- Shimojima K, Sugawara M, Shichiji M, Mukaida S, Takayama R, Imai K et al. Loss-of-function mutation of collybistin is responsible for X-linked mental retardation associated with epilepsy. J Hum Genet 2011; 56: 561–565. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

