Study of Alzheimer family case reveals hemochromotosis-associated HFE mutation
- PMID: 27081498
- PMCID: PMC4785525
- DOI: 10.1038/hgv.2014.4
Study of Alzheimer family case reveals hemochromotosis-associated HFE mutation
Abstract
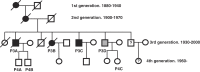
We report a family case of type II early-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD) inherited over three generations. None of the patients in the family had mutations in the genes believed to be the major risk factors for AD, such as APP, presenilin 1 or 2. Targeted exome sequencing of 249 genes that were previously reported to be associated with AD revealed a rare mutation in hemochromatosis (HFE) gene known to be associated with hemochromotosis. Compared to previous studies, we show that HFE mutation can possess the risk of AD in transferrin-, APOE- and APP-normal patients.
Figures
References
-
- Rogaev EI, Sherrington R, Rogaeva EA, Levesque G, Ikeda M, Liang Y et al. Familial Alzheimer’s disease in kindreds with missense mutations in a gene on chromosome 1 related to the Alzheimer’s disease type 3 gene. Nature 1995; 376: 775–778. - PubMed
-
- Jin SC, Pastor P, Cooper B, Cervantes S, Benitez BA, Razquin C et al. Ibero-American Alzheimer Disease Genetics Group Researchers, Cruchaga C. Pooled-DNA sequencing identifies novel causative variants in PSEN1, GRN and MAPT in a clinical early-onset and familial Alzheimer’s disease Ibero-American cohort. Alzheimers Res Ther 2012; 4: 34. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

