The many faces of KIF7
- PMID: 27081521
- PMCID: PMC4785560
- DOI: 10.1038/hgv.2015.6
The many faces of KIF7
Abstract
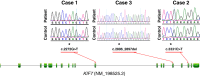
Mutations in KIF7, the gene that encodes a component of the kinesin complex of anterograde intraflagellar transport in the cilia, have been reported to cause a range of phenotypes including hydrolethalis, acrocallosal syndrome and Joubert syndrome. In a cohort of patients with various neurogenetic phenotypes, we identified novel KIF7 mutations in two families that span the known phenotypic spectrum of KIF7-related disorders. Surprisingly, we also identified a novel truncating KIF7 mutation in a third consanguineous family, in which the index presented with intellectual disability but no overt signs of ciliopathy, and his brain magnetic resonance imaging revealed an isolated dysgenesis of corpus callosum. This small cohort contributes novel pathogenic alleles of KIF7 and suggests that KIF7-related phenotypes can include isolated dysgenesis of corpus callosum with intellectual disability, thus expanding the range of phenotypes that warrant sequencing of this gene.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

