The regulatory role of interferon-γ producing gamma delta T cells via the suppression of T helper 17 cell activity in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 27083148
- PMCID: PMC4991517
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12802
The regulatory role of interferon-γ producing gamma delta T cells via the suppression of T helper 17 cell activity in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
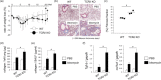
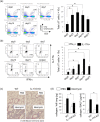
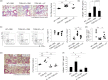
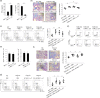
Interstitial pneumonia (IP) is a chronic progressive interstitial lung disease associated with poor prognosis and high mortality. However, the pathogenesis of IP remains to be elucidated. The aim of this study was to clarify the role of pulmonary γδT cells in IP. In wild-type (WT) mice exposed to bleomycin, pulmonary γδT cells were expanded and produced large amounts of interferon (IFN)-γ and interleukin (IL)-17A. Histological and biochemical analyses showed that bleomycin-induced IP was more severe in T cell receptor (TCR-δ-deficient (TCRδ(-/-) ) mice than WT mice. In TCRδ(-/-) mice, pulmonary IL-17A(+) CD4(+) Τ cells expanded at days 7 and 14 after bleomycin exposure. In TCRδ(-/-) mice infused with γδT cells from WT mice, the number of pulmonary IL-17A(+) CD4(+) T cells was lower than in TCRδ(-/-) mice. The examination of IL-17A(-/-) TCRδ(-/-) mice indicated that γδT cells suppressed pulmonary fibrosis through the suppression of IL-17A(+) CD4(+) T cells. The differentiation of T helper (Th)17 cells was determined in vitro, and CD4(+) cells isolated from TCRδ(-/-) mice showed normal differentiation of Th17 cells compared with WT mice. Th17 cell differentiation was suppressed in the presence of IFN-γ producing γδT cells in vitro. Pulmonary fibrosis was attenuated by IFN-γ-producing γδT cells through the suppression of pulmonary IL-17A(+) CD4(+) T cells. These results suggested that pulmonary γδT cells seem to play a regulatory role in the development of bleomycin-induced IP mouse model via the suppression of IL-17A production.
Keywords: IL-17A; gamma delta T cell; interferon-γ; interstitial pneumonia.
© 2016 British Society for Immunology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Elevated frequencies of CD4(+) IL-21(+) T, CD4(+) IL-21R(+) T and IL-21(+) Th17 cells, and increased levels of IL-21 in bleomycin-induced mice may be associated with dermal and pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2016 Apr;19(4):392-404. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12522. Epub 2014 Dec 25. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 25545680
-
Interferon-gamma regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a Th17+CD4+ T-cell-mediated graft-versus-host disease.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008 Aug 15;178(4):379-88. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200711-1648OC. Epub 2008 May 29. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18511701
-
Th17 cells and IL-17 promote the skin and lung inflammation and fibrosis process in a bleomycin-induced murine model of systemic sclerosis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016 Sep-Oct;34 Suppl 100(5):14-22. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26750756
-
Pulmonary fibrosis and type-17 immunity.Respir Investig. 2023 Sep;61(5):553-562. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2023.05.005. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Respir Investig. 2023. PMID: 37356133 Review.
-
Gamma Delta T Cells and Their Pathogenic Role in Psoriasis.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 25;12:627139. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.627139. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33732249 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Th17 cells contribute to pulmonary fibrosis and inflammation during chronic kidney disease progression after acute ischemia.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018 Feb 1;314(2):R265-R273. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00147.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29118018 Free PMC article.
-
Innate T-cell-derived IL-17A/F protects from bleomycin-induced acute lung injury but not bleomycin or adenoviral TGF-β1-induced lung fibrosis in mice.Eur J Immunol. 2024 Dec;54(12):e2451323. doi: 10.1002/eji.202451323. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Eur J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39235361 Free PMC article.
-
CD4+T and CD8+T cells profile in lung inflammation and fibrosis: targets and potential therapeutic drugs.Front Immunol. 2025 May 9;16:1562892. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1562892. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40433386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of mTORC1 Activity in CD4+ T Cells Is Associated with Lung Fibrosis and Increased γδ T Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 20;11(9):e0163288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163288. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27649073 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Fei-Xian Formula in the Treatment of Pulmonary Fibrosis on the Basis of Network Pharmacology Analysis Combined with Molecular Docking Validation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Aug 3;2021:6658395. doi: 10.1155/2021/6658395. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34394391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King TE Jr. Clinical advances in the diagnosis and therapy of the interstitial lung diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 172:268–79. - PubMed
-
- Luna MA, Bedrossian CW, Lichtiger B, Salem PA. Interstitial pneumonitis associated with bleomycin therapy. Am J Clin Pathol 1972; 58:501–10. - PubMed
-
- Braun RK, Ferrick C, Neubauer P et al IL‐17 producing gammadelta T cells are required for a controlled inflammatory response after bleomycin‐induced lung injury. Inflammation 2008; 31:167–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

