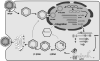
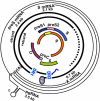
Overview of hepatitis B viral replication and genetic variability
- PMID: 27084035
- PMCID: PMC4834849
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.01.027
Overview of hepatitis B viral replication and genetic variability
Abstract
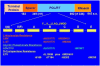
Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) greatly increases the risk for liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HBV isolates worldwide can be divided into ten genotypes. Moreover, the immune clearance phase selects for mutations in different parts of the viral genome. The outcome of HBV infection is shaped by the complex interplay of the mode of transmission, host genetic factors, viral genotype and adaptive mutations, as well as environmental factors. Core promoter mutations and mutations abolishing hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) expression have been implicated in acute liver failure, while genotypes B, C, subgenotype A1, core promoter mutations, preS deletions, C-terminal truncation of envelope proteins, and spliced pregenomic RNA are associated with HCC development. Our efforts to treat and prevent HBV infection are hampered by the emergence of drug resistant mutants and vaccine escape mutants. This paper provides an overview of the HBV life cycle, followed by review of HBV genotypes and mutants in terms of their biological properties and clinical significance.
Keywords: HBV; Replication; Variability.
Copyright © 2016 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

