DeepBlue epigenomic data server: programmatic data retrieval and analysis of epigenome region sets
- PMID: 27084938
- PMCID: PMC4987868
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw211
DeepBlue epigenomic data server: programmatic data retrieval and analysis of epigenome region sets
Abstract
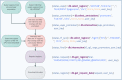
Large amounts of epigenomic data are generated under the umbrella of the International Human Epigenome Consortium, which aims to establish 1000 reference epigenomes within the next few years. These data have the potential to unravel the complexity of epigenomic regulation. However, their effective use is hindered by the lack of flexible and easy-to-use methods for data retrieval. Extracting region sets of interest is a cumbersome task that involves several manual steps: identifying the relevant experiments, downloading the corresponding data files and filtering the region sets of interest. Here we present the DeepBlue Epigenomic Data Server, which streamlines epigenomic data analysis as well as software development. DeepBlue provides a comprehensive programmatic interface for finding, selecting, filtering, summarizing and downloading region sets. It contains data from four major epigenome projects, namely ENCODE, ROADMAP, BLUEPRINT and DEEP. DeepBlue comes with a user manual, examples and a well-documented application programming interface (API). The latter is accessed via the XML-RPC protocol supported by many programming languages. To demonstrate usage of the API and to enable convenient data retrieval for non-programmers, we offer an optional web interface. DeepBlue can be openly accessed at http://deepblue.mpi-inf.mpg.de.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- The ENCODE Project Consortium. The ENCODE (ENCyclopedia Of DNA Elements) Project. Science. 2004;306:636–640. - PubMed
-
- Adams D., Altucci L., Antonarakis S.E., Ballesteros J., Beck S., Bird A., Bock C., Boehm B., Campo E., Caricasole A., et al. BLUEPRINT to decode the epigenetic signature written in blood. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012;30:224–226. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

