Influence of metabolic dysfunction on cardiac mechanics in decompensated hypertrophy and heart failure
- PMID: 27085901
- PMCID: PMC5505661
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.04.003
Influence of metabolic dysfunction on cardiac mechanics in decompensated hypertrophy and heart failure
Abstract
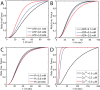
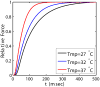
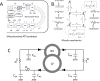
Alterations in energetic state of the myocardium are associated with decompensated heart failure in humans and in animal models. However, the functional consequences of the observed changes in energetic state on mechanical function are not known. The primary aim of the study was to quantify mechanical/energetic coupling in the heart and to determine if energetic dysfunction can contribute to mechanical failure. A secondary aim was to apply a quantitative systems pharmacology analysis to investigate the effects of drugs that target cross-bridge cycling kinetics in heart failure-associated energetic dysfunction. Herein, a model of metabolite- and calcium-dependent myocardial mechanics was developed from calcium concentration and tension time courses in rat cardiac muscle obtained at different lengths and stimulation frequencies. The muscle dynamics model accounting for the effect of metabolites was integrated into a model of the cardiac ventricles to simulate pressure-volume dynamics in the heart. This cardiac model was integrated into a simple model of the circulation to investigate the effects of metabolic state on whole-body function. Simulations predict that reductions in metabolite pools observed in canine models of heart failure can cause systolic dysfunction, blood volume expansion, venous congestion, and ventricular dilation. Simulations also predict that myosin-activating drugs may partially counteract the effects of energetic state on cross-bridge mechanics in heart failure while increasing myocardial oxygen consumption. Our model analysis demonstrates how metabolic changes observed in heart failure are alone sufficient to cause systolic dysfunction and whole-body heart failure symptoms.
Keywords: Congestive heart failure; Frank-Starling law; Metabolism; Myofilaments; Omecamtiv mecarbil.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures



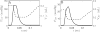


References
-
- Kwan M, Woo J, Kwok T. The standard oxygen consumption value equivalent to one metabolic equivalent (3.5 ml/min/kg) is not appropriate for elderly people. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2004;55:179–82. - PubMed
-
- Conway MA, Allis J, Ouwerkerk R, Niioka T, Rajagopalan B, Radda GK. Detection of low phosphocreatine to ATP ratio in failing hypertrophied human myocardium by 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Lancet. 1991;338:973–6. - PubMed
-
- Neubauer S, Horn M, Cramer M, Harre K, Newell JB, Peters W, et al. Myocardial phosphocreatine-to-ATP ratio is a predictor of mortality in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 1997;96:2190–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

