3D RNA and Functional Interactions from Evolutionary Couplings
- PMID: 27087444
- PMCID: PMC5024353
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.030
3D RNA and Functional Interactions from Evolutionary Couplings
Abstract
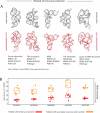
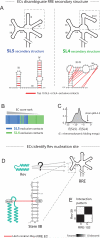
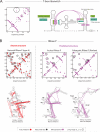
Non-coding RNAs are ubiquitous, but the discovery of new RNA gene sequences far outpaces the research on the structure and functional interactions of these RNA gene sequences. We mine the evolutionary sequence record to derive precise information about the function and structure of RNAs and RNA-protein complexes. As in protein structure prediction, we use maximum entropy global probability models of sequence co-variation to infer evolutionarily constrained nucleotide-nucleotide interactions within RNA molecules and nucleotide-amino acid interactions in RNA-protein complexes. The predicted contacts allow all-atom blinded 3D structure prediction at good accuracy for several known RNA structures and RNA-protein complexes. For unknown structures, we predict contacts in 160 non-coding RNA families. Beyond 3D structure prediction, evolutionary couplings help identify important functional interactions-e.g., at switch points in riboswitches and at a complex nucleation site in HIV. Aided by increasing sequence accumulation, evolutionary coupling analysis can accelerate the discovery of functional interactions and 3D structures involving RNA.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Bartel DP, Zapp ML, Green MR, Szostak JW. HIV-1 Rev regulation involves recognition of non-Watson-Crick base pairs in viral RNA. Cell. 1991;67:529–536. - PubMed
-
- Besag J. Statistical analysis of non-lattice data. The statistician. 1975:179–195.
-
- Butcher SE, Pyle AM. The molecular interactions that stabilize RNA tertiary structure: RNA motifs, patterns, and networks. Acc Chem Res. 2011;44:1302–1311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

