Classifying Chronic Lower Respiratory Disease Events in Epidemiologic Cohort Studies
- PMID: 27088163
- PMCID: PMC5015752
- DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201601-063OC
Classifying Chronic Lower Respiratory Disease Events in Epidemiologic Cohort Studies
Abstract
Rationale: One in 12 adults has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma. Acute exacerbations of these chronic lower respiratory diseases (CLRDs) are a major cause of morbidity and mortality. Valid approaches to classifying cases and exacerbations in the general population are needed to facilitate prevention research.
Objectives: To assess the feasibility, reproducibility, and performance of a protocol to identify CLRD cases and exacerbations triggering emergency department (ED) visits or hospitalizations in cohorts of patients derived from general populations of adults.
Methods: A protocol was developed to classify CLRD cases and severe exacerbations on the basis of review of medical records. ED and inpatient medical records were ascertained prospectively in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos, and inpatient records were retrospectively identified by administrative codes in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. "Probable" exacerbations were defined as a physician's diagnosis of CLRD with acute respiratory symptoms. "Highly probable" exacerbations additionally required systemic corticosteroid therapy, and "definite" exacerbations required airflow limitation or evidence of CLRD on imaging studies. Adjudicated results were compared with CLRD cases identified by spirometry and self-report, and with an administrative definition of exacerbations.
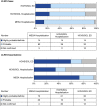
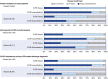
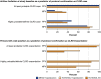
Measurements and main results: Protocol-based classification was completed independently by two physicians for 216 medical records (56 ED visits and 61 hospitalizations in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos; 99 hospitalizations in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis). Reviewer disagreement occurred in 2-5% of cases and 4-8% of exacerbations. Eighty-nine percent of records were confirmed as at least probable CLRD cases. Fifty-six percent of confirmed CLRD cases had airflow limitation on the basis of baseline study spirometry. Of records that described CLRD as the primary discharge diagnosis code, an acute exacerbation was confirmed as at least probable for 96% and as highly probable or definite for 77%. Only 50% of records with CLRD as a secondary code were confirmed, although such records accounted for over half of all confirmed exacerbations.
Conclusions: CLRD cases and severe exacerbations without preceding documentation of airflow limitation are identified frequently in population-based cohorts of persons. A primary discharge diagnosis of CLRD is specific but insensitive for defining exacerbations. Protocol-based classification of medical records may be appropriate to supplement and to validate identification of CLRD cases and exacerbations in general population studies. Clinical trials registered with www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT00005487 and NCT02060344).
Keywords: administrative data; asthma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; disease progression; incidence.
Figures

References
-
- World Health OrganizationThe top 10 causes of death [updated May 2014; accessed 2016 May 2]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/
-
- Postma DS, Rabe KF. The asthma–COPD overlap syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1241–1249. - PubMed
-
- Vestbo J, Hurd SS, Agustí AG, Jones PW, Vogelmeier C, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ, Nishimura M, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:347–365. - PubMed
-
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), National Asthma Education and Prevention ProgramExpert panel report 3: guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma. Bethesda, MD: NHLBI, National Institutes of Health; 2007 [accessed 2016 May 2]. http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/files/docs/guidelines/asthgdln.pdf
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065236/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065235/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL093081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL121457/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065234/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL129924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077612/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL125923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900013C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL130627/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065237/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122477/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES009089/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

