Differences in Genotype, Clinical Features, and Inflammatory Potential of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto Strains from Europe and the United States
- PMID: 27088349
- PMCID: PMC4861522
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2205.151806
Differences in Genotype, Clinical Features, and Inflammatory Potential of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto Strains from Europe and the United States
Abstract
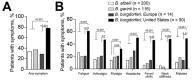
Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto isolates from patients with erythema migrans in Europe and the United States were compared by genotype, clinical features of infection, and inflammatory potential. Analysis of outer surface protein C and multilocus sequence typing showed that strains from these 2 regions represent distinct genotypes. Clinical features of infection with B. burgdorferi in Slovenia were similar to infection with B. afzelii or B. garinii, the other 2 Borrelia spp. that cause disease in Europe, whereas B. burgdorferi strains from the United States were associated with more severe disease. Moreover, B. burgdorferi strains from the United States induced peripheral blood mononuclear cells to secrete higher levels of cytokines and chemokines associated with innate and Th1-adaptive immune responses, whereas strains from Europe induced greater Th17-associated responses. Thus, strains of the same B. burgdorferi species from Europe and the United States represent distinct clonal lineages that vary in virulence and inflammatory potential.
Keywords: B. afzelii; B. garinii; Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto; Europe; Lyme borreliosis; RNA intergenic spacer type; Slovenia; United States; bacteria; clinical features; erythema migrans; genotype; inflammatory potential; multilocus sequencing typing; outer surface protein C.
Figures




References
-
- Jones KL, Muellegger RR, Means TK, Lee M, Glickstein LJ, Damle N, et al. Higher mRNA levels of chemokines and cytokines associated with macrophage activation in erythema migrans skin lesions in patients from the United States than in patients from Austria with Lyme borreliosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:85–92 . 10.1086/524022 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Strle F, Nadelman RB, Cimperman J, Nowakowski J, Picken RN, Schwartz I, et al. Comparison of culture-confirmed erythema migrans caused by Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto in New York State and by Borrelia afzelii in Slovenia. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130:32–6 . 10.7326/0003-4819-130-1-199901050-00006 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

