Comparative analysis of the GNAQ, GNA11, SF3B1, and EIF1AX driver mutations in melanoma and across the cancer spectrum
- PMID: 27089234
- PMCID: PMC5678944
- DOI: 10.1111/pcmr.12482
Comparative analysis of the GNAQ, GNA11, SF3B1, and EIF1AX driver mutations in melanoma and across the cancer spectrum
Abstract
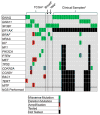
Uveal melanoma is characterized by recurrent mutations in GNAQ, GNA11, SF3B1, and EIF1AX, as well as a low total mutational burden. The frequency and clinical significance of these mutations in non-uveal melanoma and other cancers is not well described. We identified that GNAQ/GNA11 mutations occur in 0.5–1% of non-uveal melanomas and are essentially melanoma-specific. Further, these mutations are associated with a lack of other typical melanoma mutations (BRAF, NRAS, KIT, NF1), a low mutational burden, and, in a small subset, lack of response to immunotherapy. We suggest that GNAQ/GNA11 mutations characterize an uncommon but distinct subtype of non-uveal melanomas.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Carvajal RD, Sosman JA, Quevedo JF, Milhem MM, Joshua AM, Kudchadkar RR, Linette GP, Gajewski TF, Lutzky J, Lawson DH, et al. Effect of selumetinib vs chemotherapy on progression-free survival in uveal melanoma: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA : the journal of the American Medical Association. 2014;311:2397–405. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

