Droplet-based Biosensing for Lab-on-a-Chip, Open Microfluidics Platforms
- PMID: 27089377
- PMCID: PMC4931474
- DOI: 10.3390/bios6020014
Droplet-based Biosensing for Lab-on-a-Chip, Open Microfluidics Platforms
Abstract
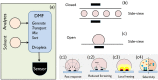
Low cost, portable sensors can transform health care by bringing easily available diagnostic devices to low and middle income population, particularly in developing countries. Sample preparation, analyte handling and labeling are primary cost concerns for traditional lab-based diagnostic systems. Lab-on-a-chip (LoC) platforms based on droplet-based microfluidics promise to integrate and automate these complex and expensive laboratory procedures onto a single chip; the cost will be further reduced if label-free biosensors could be integrated onto the LoC platforms. Here, we review some recent developments of label-free, droplet-based biosensors, compatible with "open" digital microfluidic systems. These low-cost droplet-based biosensors overcome some of the fundamental limitations of the classical sensors, enabling timely diagnosis. We identify the key challenges that must be addressed to make these sensors commercially viable and summarize a number of promising research directions.
Keywords: biosensors; droplet; early detection; high sensitivity; lab-on-a-chip; point-of-care.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A review of point-of-care (POC) and lab-on-chip (LOC) approaches in molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors for biomedical applications.Anal Chim Acta. 2025 Jul 1;1357:344080. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2025.344080. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Anal Chim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40316385 Review.
-
MIP-on-a-chip: Artificial receptors on microfluidic platforms for biomedical applications.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023 Mar 20;226:115257. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115257. Epub 2023 Jan 16. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023. PMID: 36669397 Review.
-
Lab-on-a-Chip Electrochemical Biosensors for Foodborne Pathogen Detection: A Review of Common Standards and Recent Progress.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Feb 1;13(2):215. doi: 10.3390/bios13020215. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments in optical detection technologies in lab-on-a-chip devices for biosensing applications.Sensors (Basel). 2014 Aug 21;14(8):15458-79. doi: 10.3390/s140815458. Sensors (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25196161 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Microfluidics in Liquid Crystal-Based Biosensors.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Oct 12;11(10):385. doi: 10.3390/bios11100385. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34677341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Controlling the Nucleation and Growth of Salt from Bodily Fluid for Enhanced Biosensing Applications.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Dec 6;13(12):1016. doi: 10.3390/bios13121016. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38131777 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of nanotechnology on conventional and artificial intelligence-based biosensing strategies for the detection of viruses.Discov Nano. 2023 Apr 1;18(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s11671-023-03842-4. eCollection 2023 Dec. Discov Nano. 2023. PMID: 37032711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photonic crystals: emerging biosensors and their promise for point-of-care applications.Chem Soc Rev. 2017 Jan 23;46(2):366-388. doi: 10.1039/c6cs00206d. Chem Soc Rev. 2017. PMID: 27841420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Internal flow in sessile droplets induced by substrate oscillation: towards enhanced mixing and mass transfer in microfluidic systems.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2024 Jun 24;10:86. doi: 10.1038/s41378-024-00714-4. eCollection 2024. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2024. PMID: 38919162 Free PMC article.
-
Coffee Ring Effect Enhanced Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging Biosensor via 2-λ Fitting Detection Method.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 16;14(4):195. doi: 10.3390/bios14040195. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Damhorst G.L., Murtagh M., Rodriguez W.R., Bashir R. Microfluidics and Nanotechnology for Detection of Global Infectious Diseases. Proc. IEEE. 2015;103:150–160. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2014.2385078. - DOI
-
- Suehiro J., Ohtsubo A., Hatano T., Hara M. Selective detection of bacteria by a dielectrophoretic impedance measurement method using an antibody-immobilized electrode chip. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006;119:319–326. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2005.12.027. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

