Rapid progressive long esophageal stricture caused by gastroesophageal reflux disease after pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy
- PMID: 27090811
- PMCID: PMC4836191
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-016-0137-2
Rapid progressive long esophageal stricture caused by gastroesophageal reflux disease after pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy
Abstract
Background: Delayed gastric emptying (DGE) is a major postoperative complication after pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy (PpPD) and sometimes causes reflux esophagitis. In most cases, this morbidity is controllable by proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) and very rarely results in esophageal stricture. Balloon dilation is usually performed for benign esophageal stricture, and esophagectomy was rarely elected. In the present case, there were two important problems of surgical procedure; how to perform esophageal reconstruction after PpPD and whether to preserve the stomach or not.
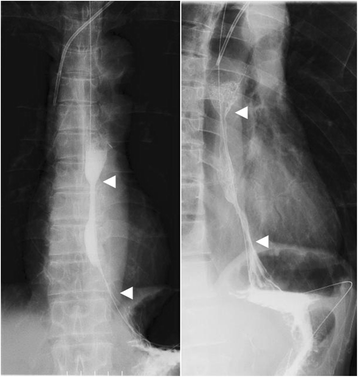
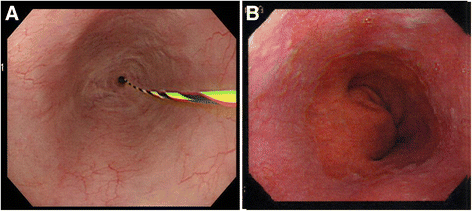
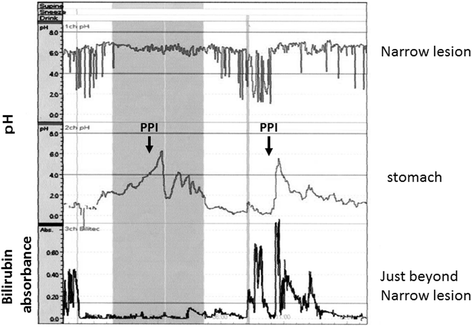
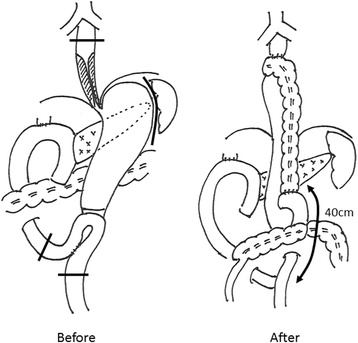
Case presentation: A 63-year-old man underwent PpPD and Child reconstruction with Braun anastomosis for lower bile duct carcinoma. Two weeks after surgery DGE occurred, and a 10 cm long stricture from middle esophagus to cardia developed one and a half month after surgery in spite of the administration of antacids. Balloon dilation was performed, but perforation occurred. It was recovered with conservative treatment. Even the administration of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) for approximately five mouths did not improve esophageal stricture. Simultaneous 24-h pH and bilirubin monitoring confirmed that this patient was resistant to PPI. We performed middle-lower esophagectomy with total gastrectomy to prevent gastric acid from injuring reconstructed organ and remnant esophagus through a right thoracoabdominal incision, and we also performed reconstruction with transverse colon, adding Roux-Y anastomosis, to prevent bile reflux to the remnant esophagus. Minor leakage developed during the postoperative course but was soon cured by conservative treatment. The patient started oral intake on the 25th postoperative day (POD) and was discharged on the 34th POD in good condition.
Conclusion: Long esophageal stricture after PpPD was successfully treated by middle-lower esophagectomy and total gastrectomy with transverse colon reconstruction through a right thoracoabdominal incision. Conventional PD or SSPPD with Roux-en Y reconstruction rather than PpPD should be selected to reduce the risk of DGE and prevent bile reflux, in performing PD for patients with hiatal hernia or rapid metabolizer CYP2C19 genotype; otherwise, fundoplication such as Nissen and Toupet should be added.
Keywords: Delayed gastric emptying; Esophageal stricture; Esophagectomy; Pancreatoduodenectomy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does antecolic reconstruction decrease delayed gastric emptying after pancreatoduodenectomy?World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Dec 7;18(45):6527-31. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i45.6527. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23236224 Free PMC article.
-
An antecolic Roux-en Y type reconstruction decreased delayed gastric emptying after pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy.J Gastrointest Surg. 2008 Jun;12(6):1081-6. doi: 10.1007/s11605-008-0483-1. Epub 2008 Feb 7. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008. PMID: 18256885
-
The surgical procedure and clinical results of subtotal stomach preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy (SSPPD) in comparison with pylorus preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy (PPPD).J Surg Oncol. 2007 Feb 1;95(2):106-9. doi: 10.1002/jso.20608. J Surg Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17262740
-
Functional disorders and quality of life after esophagectomy and gastric tube reconstruction for cancer.J Visc Surg. 2011 Oct;148(5):e327-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2011.09.001. Epub 2011 Oct 22. J Visc Surg. 2011. PMID: 22019835 Review.
-
Pancreaticoduodenectomy versus pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy: the clinical impact of a new surgical procedure; pylorus-resecting pancreaticoduodenectomy.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011 Nov;18(6):755-61. doi: 10.1007/s00534-011-0427-0. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011. PMID: 21861144 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of CYP2C19 metabolizer status on esophageal mucosal inflammation, acid exposure, and motility among patients on chronic proton-pump inhibitor therapy with refractory symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease.J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2024 Feb 10;7(3):238-245. doi: 10.1093/jcag/gwae005. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38841142 Free PMC article.
-
Lung function parameters in patients with gastroesophageal reflux without respiratory symptoms: a case-control study.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2019 Fall;12(4):287-291. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2019. PMID: 31749916 Free PMC article.
-
Successful staged surgery for advanced esophageal cancer after conversion pancreatoduodenectomy with pancreaticogastrostomy.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr;18(2):249-257. doi: 10.1007/s12328-025-02093-3. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39808362 Free PMC article.
-
Esophageal reconstruction using a pedicled jejunum following esophagectomy for metastatic esophageal stricture from breast cancer in a patient with previous pancreatoduodenectomy.Nagoya J Med Sci. 2019 Nov;81(4):679-685. doi: 10.18999/nagjms.81.4.679. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31849385 Free PMC article.
-
Subtotal esophagectomy and concurrent reconstruction with free jejunal flap for primary esophageal cancer after pancreatoduodenectomy.Surg Case Rep. 2024 May 22;10(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s40792-024-01919-5. Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38775882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakai T, Kawabe T, Shiraishi O, Okuno K, Shiozaki H. Pylorotomy in pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 2006;53(72):947–9. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DA, Stacy T, Ryan M, Wootton T, Willis J, Hornbuckle K, et al. A comparison of esomeprazole and lansoprazole for control of intragastric pH in patients with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;22(2):129–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02534.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

