ZRF1 mediates remodeling of E3 ligases at DNA lesion sites during nucleotide excision repair
- PMID: 27091446
- PMCID: PMC5084270
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201506099
ZRF1 mediates remodeling of E3 ligases at DNA lesion sites during nucleotide excision repair
Abstract
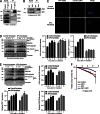
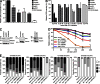
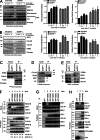
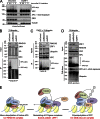
Faithful DNA repair is essential to maintain genome integrity. Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation elicits both the recruitment of DNA repair factors and the deposition of histone marks such as monoubiquitylation of histone H2A at lesion sites. Here, we report how a ubiquitin E3 ligase complex specific to DNA repair is remodeled at lesion sites in the global genome nucleotide excision repair (GG-NER) pathway. Monoubiquitylation of histone H2A (H2A-ubiquitin) is catalyzed predominantly by a novel E3 ligase complex consisting of DDB2, DDB1, CUL4B, and RING1B (UV-RING1B complex) that acts early during lesion recognition. The H2A-ubiquitin binding protein ZRF1 mediates remodeling of this E3 ligase complex directly at the DNA lesion site, causing the assembly of the UV-DDB-CUL4A E3 ligase complex (DDB1-DDB2-CUL4A-RBX1). ZRF1 is an essential factor in GG-NER, and its function at damaged chromatin sites is linked to damage recognition factor XPC. Overall, the results shed light on the interplay between epigenetic and DNA repair recognition factors at DNA lesion sites.
© 2016 Gracheva et al.
Figures
Comment in
-
DNA damage response: Controlling ubiquitylation at DNA lesions.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Jun;17(6):329. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.59. Epub 2016 May 5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27145722 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The cullin 4B-based UV-damaged DNA-binding protein ligase binds to UV-damaged chromatin and ubiquitinates histone H2A.Cancer Res. 2008 Jul 1;68(13):5014-22. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6162. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18593899
-
The DDB1-CUL4ADDB2 ubiquitin ligase is deficient in xeroderma pigmentosum group E and targets histone H2A at UV-damaged DNA sites.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Feb 21;103(8):2588-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511160103. Epub 2006 Feb 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16473935 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage binding protein component DDB1 participates in nucleotide excision repair through DDB2 DNA-binding and cullin 4A ubiquitin ligase activity.Cancer Res. 2006 Sep 1;66(17):8590-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1115. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16951172
-
Damage-specific DNA binding protein 1 (DDB1): a protein with a wide range of functions.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Dec;43(12):1664-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.09.001. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21959250 Review.
-
UV-induced ubiquitylation of XPC complex, the UV-DDB-ubiquitin ligase complex, and DNA repair.J Mol Histol. 2006 Sep;37(5-7):189-202. doi: 10.1007/s10735-006-9044-7. Epub 2006 Jul 21. J Mol Histol. 2006. PMID: 16858626 Review.
Cited by
-
PARP1-dependent recruitment of the FBXL10-RNF68-RNF2 ubiquitin ligase to sites of DNA damage controls H2A.Z loading.Elife. 2018 Jul 9;7:e38771. doi: 10.7554/eLife.38771. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29985131 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of DNA Repair Mechanisms: How the Chromatin Environment Regulates the DNA Damage Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Aug 5;18(8):1715. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081715. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28783053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mRNA Processing Factor CstF-50 and Ubiquitin Escort Factor p97 Are BRCA1/BARD1 Cofactors Involved in Chromatin Remodeling during the DNA Damage Response.Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Jan 29;38(4):e00364-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00364-17. Print 2018 Feb 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29180510 Free PMC article.
-
Zuo1 supports G4 structure formation and directs repair toward nucleotide excision repair.Nat Commun. 2020 Aug 6;11(1):3907. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17701-8. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32764578 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleotide excision repair leaves a mark on chromatin: DNA damage detection in nucleosomes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(24):7925-7942. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03984-7. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34731255 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Angers S., Li T., Yi X., MacCoss M.J., Moon R.T., and Zheng N.. 2006. Molecular architecture and assembly of the DDB1-CUL4A ubiquitin ligase machinery. Nature. 443:590–593. - PubMed
-
- Araki M., Masutani C., Takemura M., Uchida A., Sugasawa K., Kondoh J., Ohkuma Y., and Hanaoka F.. 2001. Centrosome protein centrin 2/caltractin 1 is part of the xeroderma pigmentosum group C complex that initiates global genome nucleotide excision repair. J. Biol. Chem. 276:18665–18672. 10.1074/jbc.M100855200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bergink S., Salomons F.A., Hoogstraten D., Groothuis T.A., de Waard H., Wu J., Yuan L., Citterio E., Houtsmuller A.B., Neefjes J., et al. . 2006. DNA damage triggers nucleotide excision repair-dependent monoubiquitylation of histone H2A. Genes Dev. 20:1343–1352. 10.1101/gad.373706 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

