SEMG signal compression based on two-dimensional techniques
- PMID: 27091454
- PMCID: PMC4835940
- DOI: 10.1186/s12938-016-0158-1
SEMG signal compression based on two-dimensional techniques
Abstract
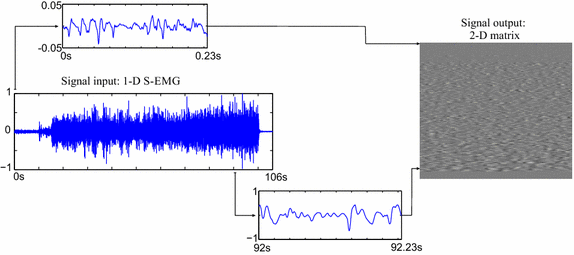
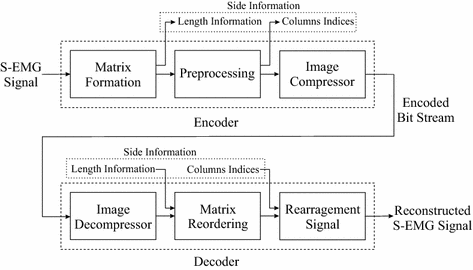
Background: Recently, two-dimensional techniques have been successfully employed for compressing surface electromyographic (SEMG) records as images, through the use of image and video encoders. Such schemes usually provide specific compressors, which are tuned for SEMG data, or employ preprocessing techniques, before the two-dimensional encoding procedure, in order to provide a suitable data organization, whose correlations can be better exploited by off-the-shelf encoders. Besides preprocessing input matrices, one may also depart from those approaches and employ an adaptive framework, which is able to directly tackle SEMG signals reassembled as images.
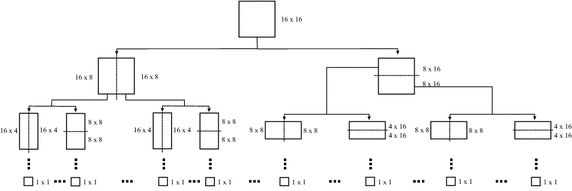
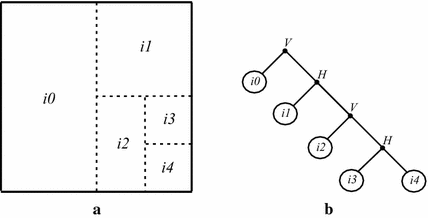
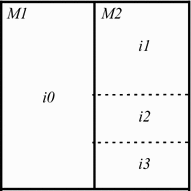
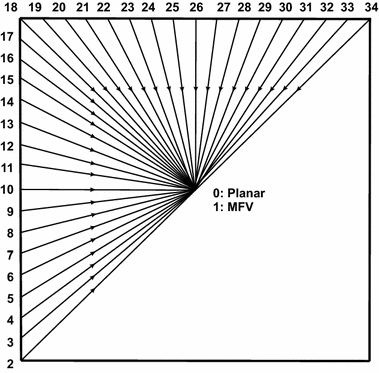
Methods: This paper proposes a new two-dimensional approach for SEMG signal compression, which is based on a recurrent pattern matching algorithm called multidimensional multiscale parser (MMP). The mentioned encoder was modified, in order to efficiently work with SEMG signals and exploit their inherent redundancies. Moreover, a new preprocessing technique, named as segmentation by similarity (SbS), which has the potential to enhance the exploitation of intra- and intersegment correlations, is introduced, the percentage difference sorting (PDS) algorithm is employed, with different image compressors, and results with the high efficiency video coding (HEVC), H.264/AVC, and JPEG2000 encoders are presented.
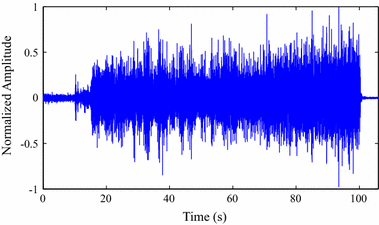
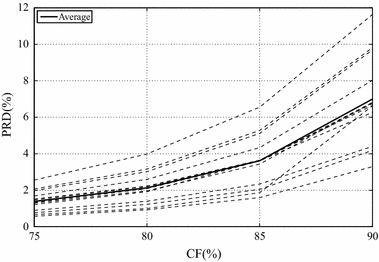
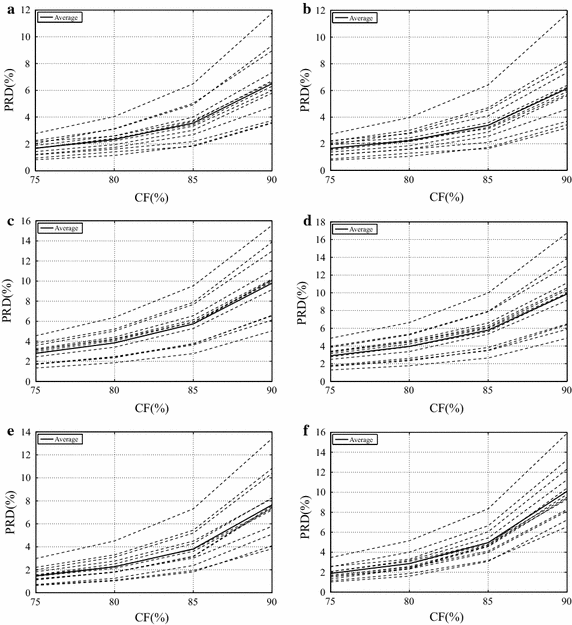
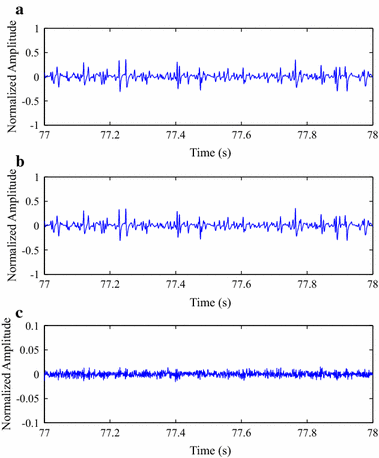
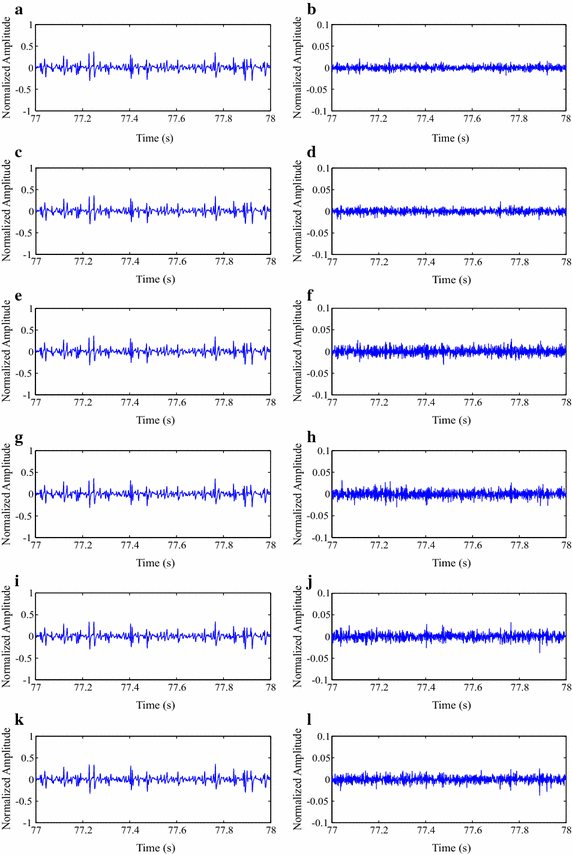
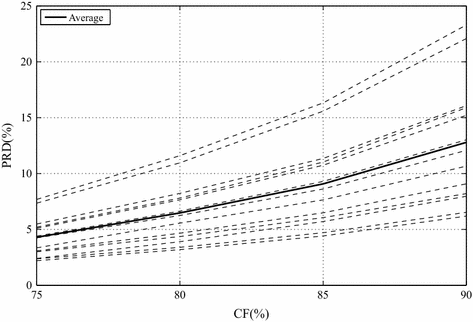
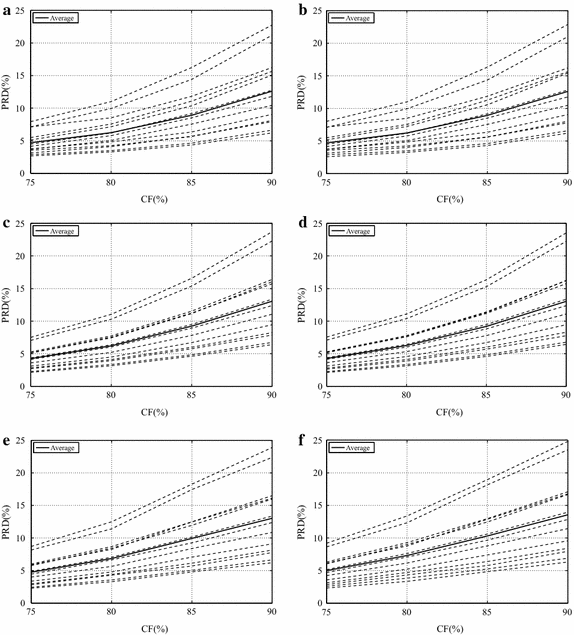
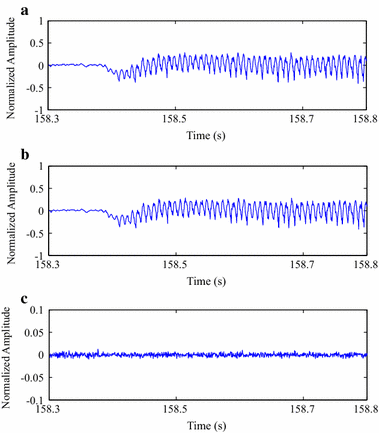
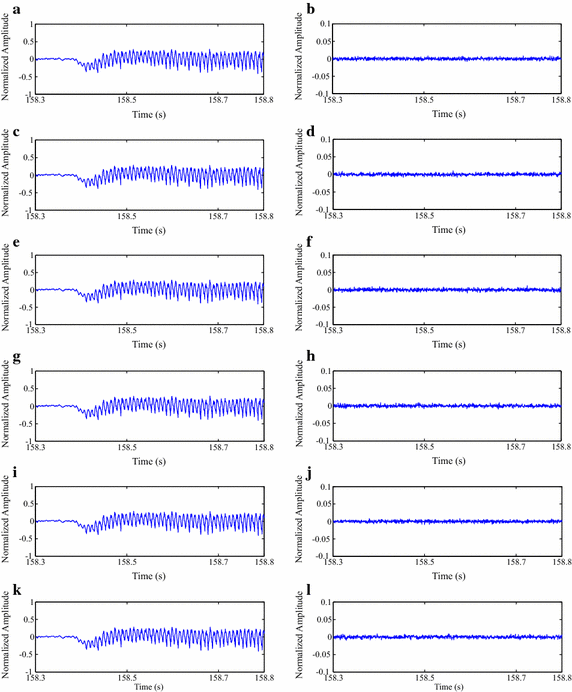
Results: Experiments were carried out with real isometric and dynamic records, acquired in laboratory. Dynamic signals compressed with H.264/AVC and HEVC, when combined with preprocessing techniques, resulted in good percent root-mean-square difference [Formula: see text] compression factor figures, for low and high compression factors, respectively. Besides, regarding isometric signals, the modified two-dimensional MMP algorithm outperformed state-of-the-art schemes, for low compression factors, the combination between SbS and HEVC proved to be competitive, for high compression factors, and JPEG2000, combined with PDS, provided good performance allied to low computational complexity, all in terms of percent root-mean-square difference [Formula: see text] compression factor.
Conclusion: The proposed schemes are effective and, specifically, the modified MMP algorithm can be considered as an interesting alternative for isometric signals, regarding traditional SEMG encoders. Besides, the approach based on off-the-shelf image encoders has the potential of fast implementation and dissemination, given that many embedded systems may already have such encoders available, in the underlying hardware/software architecture.
Keywords: HEVC; Multidimensional multiscale parser; Preprocessing technique; SEMG.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Electromyographic signal compression based on preprocessing techniques.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012;2012:5404-7. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6347216. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012. PMID: 23367151
-
Two-dimensional compression of surface electromyographic signals using column-correlation sorting and image encoders.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009;2009:428-31. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5333134. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009. PMID: 19963967
-
On EMG signal compression with recurrent patterns.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2008 Jul;55(7):1920-3. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2008.919729. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2008. PMID: 18595812
-
Video traffic characteristics of modern encoding standards: H.264/AVC with SVC and MVC extensions and H.265/HEVC.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014 Feb 20;2014:189481. doi: 10.1155/2014/189481. eCollection 2014. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 24701145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gesture Recognition Using Surface Electromyography and Deep Learning for Prostheses Hand: State-of-the-Art, Challenges, and Future.Front Neurosci. 2021 Apr 26;15:621885. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.621885. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33981195 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdaheer MS. Digital signal processing. Hoboken: Laxmi Publications; 2007.
-
- Li N, Li P. An improved algorithm based on EMD-wavelet for ECG signal de-noising. In: Proceedings of the international joint conference on computational sciences and optimization. 2009. p. 825–827.
-
- Phinyomark A, Limsakul C, Phukpattaranont P. Application of wavelet analysis in EMG feature extraction for pattern classification. Meas Sci Rev. 2011;11(2):45–52. doi: 10.2478/v10048-011-0009-y. - DOI
-
- Peker M, Sen B, Delen D. A novel method for automated diagnosis of epilepsy using complex-valued classifiers. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2015;99:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Merletti R, Parker P. Electromyography: engineering and noninvasive applications. Hoboken: Wiley; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

