Photosynthesis-related characteristics of the midrib and the interveinal lamina in leaves of the C3-CAM intermediate plant Mesembryanthemum crystallinum
- PMID: 27091507
- PMCID: PMC4904173
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcw049
Photosynthesis-related characteristics of the midrib and the interveinal lamina in leaves of the C3-CAM intermediate plant Mesembryanthemum crystallinum
Abstract
Background and aims: Leaf veins are usually encircled by specialized bundle sheath cells. In C4 plants, they play an important role in CO2 assimilation, and the photosynthetic activity is compartmentalized between the mesophyll and the bundle sheath. In C3 and CAM (Crassulacean acid metabolism) plants, the photosynthetic activity is generally attributed to the leaf mesophyll cells, and the vascular parenchymal cells are rarely considered for their role in photosynthesis. Recent studies demonstrate that enzymes required for C4 photosynthesis are also active in the veins of C3 plants, and their vascular system contains photosynthetically competent parenchyma cells. However, our understanding of photosynthesis in veins of C3 and CAM plants still remains insufficient. Here spatial analysis of photosynthesis-related properties were applied to the midrib and the interveinal lamina cells in leaves of Mesembryanthemum crystallinum, a C3-CAM intermediate plant.
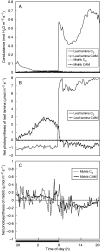
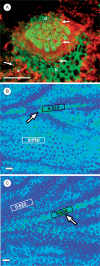
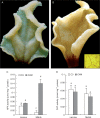
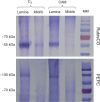
Methods: The midrib anatomy as well as chloroplast structure and chlorophyll fluorescence, diurnal gas exchange profiles, the immunoblot patterns of PEPC (phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase) and RubisCO (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase), H2O2 localization and antioxidant enzyme activities were compared in the midrib and in the interveinal mesophyll cells in leaves of C3 and CAM plants.
Key results: Leaf midribs were structurally competent to perform photosynthesis in C3 and CAM plants. The midrib chloroplasts resembled those in the bundle sheath cells of C4 plants and were characterized by limited photosynthetic activity.
Conclusions: The metabolic roles of midrib chloroplasts differ in C3 and CAM plants. It is suggested that in leaves of C3 plants the midrib chloroplasts could be involved in the supply of CO2 for carboxylation, and in CAM plants they could provide malate to different metabolic processes and mediate H2O2 signalling.
Keywords: Antioxidant enzymes; Mesembryanthemum crystallinum; chloroplast structure; gas exchange; interveinal lamina tissues; midrib; photosynthetic/photochemical activity.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Annals of Botany Company. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson JM, Chow WS, De Las Rivas J. 2008.. Dynamic flexibility in the structure and function of photosystem II in higher plant thylakoid membranes: the grana enigma. Photosynthesis Research 98: 575–587. - PubMed
-
- Aschan G, Pfanz H. 2003.. Non-foliar photosynthesis – a strategy of additional carbon acquisition. Flora 198: 81–97.
-
- Berveiller D, Damesin C. 2008.. Carbon assimilation by tree stems: potential involvement of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. Trees 22: 149–157.
-
- Bradford MM. 1976.. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry 72: 248–254. - PubMed
-
- Brown NJ, Palmer BG, Stanley S, et al. 2010.. C4 acid decarboxylases required for C4 photosynthesis are active in the mid-vein of the C3 species Arabidopsis thaliana, and are important in sugar and amino acid metabolism. The Plant Journal 61: 122–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

