Curcumin mediates oxaliplatin-acquired resistance reversion in colorectal cancer cell lines through modulation of CXC-Chemokine/NF-κB signalling pathway
- PMID: 27091625
- PMCID: PMC4835769
- DOI: 10.1038/srep24675
Curcumin mediates oxaliplatin-acquired resistance reversion in colorectal cancer cell lines through modulation of CXC-Chemokine/NF-κB signalling pathway
Abstract
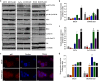
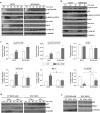
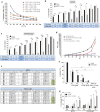
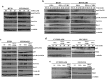
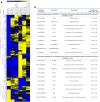
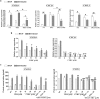
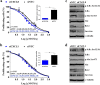
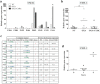
Resistance to oxaliplatin (OXA) is a complex process affecting the outcomes of metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) patients treated with this drug. De-regulation of the NF-κB signalling pathway has been proposed as an important mechanism involved in this phenomenon. Here, we show that NF-κB was hyperactivated in in vitro models of OXA-acquired resistance but was attenuated by the addition of Curcumin, a non-toxic NF-κB inhibitor. The concomitant combination of Curcumin + OXA was more effective and synergistic in cell lines with acquired resistance to OXA, leading to the reversion of their resistant phenotype, through the inhibition of the NF-κB signalling cascade. Transcriptomic profiling revealed the up-regulation of three NF-κB-regulated CXC-chemokines, CXCL8, CXCL1 and CXCL2, in the resistant cells that were more efficiently down-regulated after OXA + Curcumin treatment as compared to the sensitive cells. Moreover, CXCL8 and CXCL1 gene silencing made resistant cells more sensitive to OXA through the inhibition of the Akt/NF-κB pathway. High expression of CXCL1 in FFPE samples from explant cultures of CRC patients-derived liver metastases was associated with response to OXA + Curcumin. In conclusion, we suggest that combination of OXA + Curcumin could be an effective treatment, for which CXCL1 could be used as a predictive marker, in CRC patients.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

