How to Acquire Cardiac Volumes for Sonographic Examination of the Fetal Heart: Part 2
- PMID: 27091912
- PMCID: PMC8475629
- DOI: 10.7863/ultra.16.01082
How to Acquire Cardiac Volumes for Sonographic Examination of the Fetal Heart: Part 2
Abstract
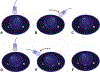
The effective performance of fetal cardiac examination using spatiotemporal image correlation (STIC) technology requires 2 essential steps: volume acquisition and postprocessing. An important prerequisite is training sonologists to acquire high-quality volume data sets so that when analyzed, such volumes are informative. This article is part 2 of a series on 4-dimensional sonography with STIC. Part 1 focused on STIC technology and its features, the importance of operator training/experience and acquisition of high-quality STIC volumes, factors that affect STIC volume acquisition rates, and general recommendations on performing 4D sonography with STIC. In part 2, we discuss a detailed and practical stepwise approach for STIC volume acquisition, along with methods to determine whether such volumes are appropriate for analysis.
Keywords: 4-dimensional; STICLoop; fetal echocardiography; fetus; spatiotemporal image correlation; ultrasound.
© 2016 by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine.
Figures
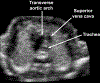


References
-
- Viñals F, Poblete P, Giuliano A. Spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC): a new tool for the prenatal screening of congenital heart defects. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003; 22: 388–394. - PubMed
-
- DeVore GR, Falkensammer P, Sklansky MS, Platt LD. Spatiotemporal image correlation (STIC): new technology for evaluation of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003; 22: 380–387. - PubMed
-
- Gonçalves LF, Lee W, Chaiworapongsa T, et al.Four-dimensional ultrasonography of the fetal heart with spatiotemporal image correlation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003; 189: 1792–1802. - PubMed
-
- Chaoui R, Hoffmann J, Heling KS. Three-dimensional (3D) and 4D color Doppler fetal echocardiography using spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC). Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 23: 535–545. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

