Clusters of circulating tumor cells traverse capillary-sized vessels
- PMID: 27091969
- PMCID: PMC4983862
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1524448113
Clusters of circulating tumor cells traverse capillary-sized vessels
Abstract
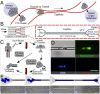
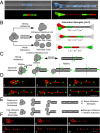
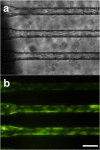
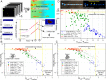
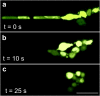
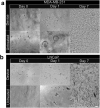
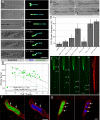
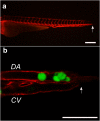
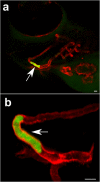
Multicellular aggregates of circulating tumor cells (CTC clusters) are potent initiators of distant organ metastasis. However, it is currently assumed that CTC clusters are too large to pass through narrow vessels to reach these organs. Here, we present evidence that challenges this assumption through the use of microfluidic devices designed to mimic human capillary constrictions and CTC clusters obtained from patient and cancer cell origins. Over 90% of clusters containing up to 20 cells successfully traversed 5- to 10-μm constrictions even in whole blood. Clusters rapidly and reversibly reorganized into single-file chain-like geometries that substantially reduced their hydrodynamic resistances. Xenotransplantation of human CTC clusters into zebrafish showed similar reorganization and transit through capillary-sized vessels in vivo. Preliminary experiments demonstrated that clusters could be disrupted during transit using drugs that affected cellular interaction energies. These findings suggest that CTC clusters may contribute a greater role to tumor dissemination than previously believed and may point to strategies for combating CTC cluster-initiated metastasis.
Keywords: CTC clusters; cancer metastasis; capillary microhemodynamics; circulating tumor cell cluster microemboli; microfluidics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Krebs MG, et al. Molecular analysis of circulating tumour cells—biology and biomarkers. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014;11(3):129–144. - PubMed
-
- Paterlini-Brechot P, Benali NL. Circulating tumor cells (CTC) detection: Clinical impact and future directions. Cancer Lett. 2007;253(2):180–204. - PubMed
-
- Hou JM, et al. Clinical significance and molecular characteristics of circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor microemboli in patients with small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(5):525–532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

