Comparative systems pharmacology of HIF stabilization in the prevention of retinopathy of prematurity
- PMID: 27091985
- PMCID: PMC4983815
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1523005113
Comparative systems pharmacology of HIF stabilization in the prevention of retinopathy of prematurity
Abstract
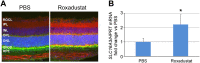
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) causes 100,000 new cases of childhood blindness each year. ROP is initiated by oxygen supplementation necessary to prevent neonatal death. We used organ systems pharmacology to define the transcriptomes of mice that were cured of oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR, ROP model) by hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) stabilization via HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibition using the isoquinolone Roxadustat or the 2-oxoglutarate analog dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG). Although both molecules conferred a protective phenotype, gene expression analysis by RNA sequencing found that Roxadustat can prevent OIR by two pathways: direct retinal HIF stabilization and induction of aerobic glycolysis or indirect hepatic HIF-1 stabilization and increased serum angiokines. As predicted by pathway analysis, Roxadustat rescued the hepatic HIF-1 knockout mouse from retinal oxygen toxicity, whereas DMOG could not. The simplicity of systemic treatment that targets both the liver and the eye provides a rationale for protecting the severely premature infant from oxygen toxicity.
Keywords: BPD; HIF; ROP; Roxadustat; prolyl hydroxylase inhibition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

