Exploring the Secretomes of Microbes and Microbial Communities Using Filamentous Phage Display
- PMID: 27092113
- PMCID: PMC4823517
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00429
Exploring the Secretomes of Microbes and Microbial Communities Using Filamentous Phage Display
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Exploring the Secretomes of Microbes and Microbial Communities Using Filamentous Phage Display.Front Microbiol. 2016 Jun 14;7:927. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00927. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27379057 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Microbial surface and secreted proteins (the secretome) contain a large number of proteins that interact with other microbes, host and/or environment. These proteins are exported by the coordinated activities of the protein secretion machinery present in the cell. A group of bacteriophage, called filamentous phage, have the ability to hijack bacterial protein secretion machinery in order to amplify and assemble via a secretion-like process. This ability has been harnessed in the use of filamentous phage of Escherichia coli in biotechnology applications, including screening large libraries of variants for binding to "bait" of interest, from tissues in vivo to pure proteins or even inorganic substrates. In this review we discuss the roles of secretome proteins in pathogenic and non-pathogenic bacteria and corresponding secretion pathways. We describe the basics of phage display technology and its variants applied to discovery of bacterial proteins that are implicated in colonization of host tissues and pathogenesis, as well as vaccine candidates through filamentous phage display library screening. Secretome selection aided by next-generation sequence analysis was successfully applied for selective display of the secretome at a microbial community scale, the latter revealing the richness of secretome functions of interest and surprising versatility in filamentous phage display of secretome proteins from large number of Gram-negative as well as Gram-positive bacteria and archaea.
Keywords: adhesins; bacteriophage; metagenomics; next generation sequencing; phage display; secretome.
Figures
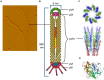
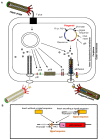
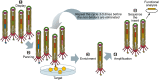


References
-
- Abruquah H. H. (2009). Identification of Host-pathogen Interacting Molecules of Campylobacter Jejuni Using Phage Display Technology and In silico Sequence Analysis. Ph.D. thesis, submitted to the University of Nottingham for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Microbiology, The University of Nottingham, Nottingham.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

