Survey of pharmacy involvement in hospital medication reconciliation programs across the United States
- PMID: 27092258
- PMCID: PMC4822532
- DOI: 10.1177/2050312115615147
Survey of pharmacy involvement in hospital medication reconciliation programs across the United States
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study is to conduct a review of pertinent literature, assess pharmacy involvement in medication reconciliation, and offer insight into best practices for hospitals to implement and enhance their medication reconciliation programs.
Method: Pharmacists in hospitals nationwide were asked to complete an anonymous survey via the American College of Clinical Pharmacy online database. The multiple choice survey analyzed the roles that healthcare professionals play in medication reconciliation programs at hospitals.
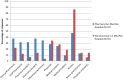
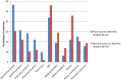
Results: Of the survey responses received, 32/91 (35%) came from pharmacists at hospitals with a pharmacy-led medication reconciliation program. Of these pharmacy-led programs, 17/32 (53%) have a dedicated pharmacist or pharmacy staff to perform medication reconciliation.
Conclusion: A comprehensive review of literature suggests that pharmacy involvement has the potential to reduce medication reconciliation errors and may improve patient satisfaction. Focused, full-time medication reconciliation pharmacists can help hospitals save time and money, improve outcomes, and meet higher standards issued by the Joint Commission. Data obtained in this study show the extent to which pharmacists contribute to achieving these goals in healthcare systems nationwide. This baseline study provides a strong case for hospitals to implement a pharmacy-led medication reconciliation program.
Keywords: Pharmacoepidemiology/drug safety; epidemiology/public health; pharmacoeconomics/health economics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- National Patient Safety Goals (NPSG 03.06.01). Joint Commission Online (A complimentary publication of the Joint Commission), 8 December 2010; National Patient Safety Goals: 2011 Updates, Lisa Schulmeister (published online: Friday, 4 March 2011).
-
- Mansur J, Adamski P, Small R. The Joint Commission update for 2014. In: ASHP midyear clinical meeting, Orlando, Florida, 11 December 2013.
-
- Soler-Giner E, Izuel-Rami M, Villar-Fernández I, et al. Quality of home medication collection in the ED: reconciliation discrepancies. Farm Hosp 2011; 35(4): 165–171. - PubMed
-
- Bishop MA, Cohen BA, Billings LK, et al. Reduction errors through discharge medication reconciliation by pharmacy services. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2015; 72(17 Suppl. 2): S120–S126. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources