Profilings of MicroRNAs in the Liver of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Infected with Flavobacterium columnare
- PMID: 27092486
- PMCID: PMC4849022
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17040566
Profilings of MicroRNAs in the Liver of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Infected with Flavobacterium columnare
Abstract
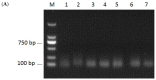
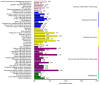
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles in regulation of many biological processes in eukaryotes, including pathogen infection and host interactions. Flavobacterium columnare (FC) infection can cause great economic loss of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) which is one of the most important cultured fish in the world. However, miRNAs in response to FC infection in common carp has not been characterized. To identify specific miRNAs involved in common carp infected with FC, we performed microRNA sequencing using livers of common carp infected with and without FC. A total of 698 miRNAs were identified, including 142 which were identified and deposited in the miRbase database (Available online: http://www.mirbase.org/) and 556 had only predicted miRNAs. Among the deposited miRNAs, eight miRNAs were first identified in common carp. Thirty of the 698 miRNAs were differentially expressed miRNAs (DIE-miRNAs) between the FC infected and control samples. From the DIE-miRNAs, seven were selected randomly and their expression profiles were confirmed to be consistent with the microRNA sequencing results using RT-PCR and qRT-PCR. In addition, a total of 27,363 target genes of the 30 DIE-miRNAs were predicted. The target genes were enriched in five Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways, including focal adhesion, extracellular matrix (ECM)-receptor interaction, erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog (ErbB) signaling pathway, regulation of actin cytoskeleton, and adherent junction. The miRNA expression profile of the liver of common carp infected with FC will pave the way for the development of effective strategies to fight against FC infection.
Keywords: Flavobacterium columnare; common carp; deep sequencing; liver; miRNA.
Figures



References
-
- Zhou W., Zhang Y., Wen Y., Ji W., Zhou Y., Ji Y., Liu X., Wang W., Asim M., Liang X., et al. Analysis of the transcriptomic profilings of Mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) infected with Flavobacterium columnare with an emphasis on immune responses. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015;43:111–119. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2014.12.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Declercq A.M., Chiers K., van den Broeck W., Eeckhaut V., Cornelissen M., Bossier P., Haesebrouck F., Decostere A. Interactions of highly and low virulent Flavobacterium columnare isolates with gill tissue in carp and rainbow trout. Vet. Res. 2015;46 doi: 10.1186/s13567-015-0164-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

