Exposure to Hyperbaric Oxygen Intensified Vancomycin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats
- PMID: 27092557
- PMCID: PMC4836689
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152554
Exposure to Hyperbaric Oxygen Intensified Vancomycin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats
Abstract
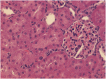
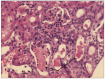
It has been suggested that oxidative stress is a potential mechanism for vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity and hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO) has been shown to be effective in treating renal toxicity that has been pharmacologically induced in animal models. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of HBO therapy on vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. The study group comprised 36 Sprague Dawley male rats. We treated 30 with 500 mg/kg of intraperitoneal vancomycin once a day for 7 days. Half of these rats received a daily 1-hour treatment with HBO at 2 Atmospheres (ATM) on the same 7 days and formed the HBO+ group. The other 15 subjects received no HBO treatment (HBO- group). The remaining six rats served as the control group, three received HBO treatments alone and no treatment was administered to the other three rats. Laboratory results were obtained on day 8 and the intervention and control groups were compared. Rats in the HBO+ group gained less weight than the HBO- group (11.6 grams vs 22.6 grams; P = 0,008) and had significantly higher serum blood urea nitrogen (99.6 vs 52.6 mg/dL; P<0.001), serum creatinine (0.42 vs 0.16 mg/dL; P = 0.001) and magnesium (3.6 vs 3.1 mg/dL; P = 0.014). The vancomycin blood levels were also higher in the HBO+ group (27.8 vs 6.7 μg/mL; P = 0.078). There were no pathological kidney changes in the control group. All the kidneys from the treated groups (vancomycin +HBO and vancomycin HBO-) showed moderate to severe histopathological changes with no statistical significance between them. This study demonstrated that exposure to hyperbaric oxygen intensified vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
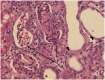
Similar articles
-
Effects of different doses of hyperbaric oxygen on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity.Ren Fail. 2007;29(3):257-63. doi: 10.1080/08860220601166487. Ren Fail. 2007. PMID: 17497437
-
Investigation of the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats.Arch Toxicol. 2005 May;79(5):289-93. doi: 10.1007/s00204-004-0627-3. Epub 2004 Nov 9. Arch Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 15902426
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats.Urol Int. 2007;78(1):82-5. doi: 10.1159/000096941. Urol Int. 2007. PMID: 17192739
-
Nephroprotective effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in murine models of acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Life Sci. 2024 Nov 15;357:123098. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123098. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39362585
-
Genotoxicity of hyperbaric oxygen.Mutat Res. 2002 Dec;512(2-3):111-9. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5742(02)00045-5. Mutat Res. 2002. PMID: 12464346 Review.
Cited by
-
Local Application of Vancomycin in One-Stage Revision of Prosthetic Joint Infection Caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Aug 17;65(9):e0030321. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00303-21. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 34181479 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperbaric Oxygenation: Can It Be a Novel Supportive Method in Acute Kidney Injury? Data Obtained from Experimental Studies.Cells. 2024 Jun 28;13(13):1119. doi: 10.3390/cells13131119. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38994971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effects of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Rosa canina Fruit on Vancomycin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats.J Toxicol. 2021 May 28;2021:5525714. doi: 10.1155/2021/5525714. eCollection 2021. J Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34135957 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-articular versus systemic vancomycin for the treatment of periprosthetic joint infection after debridement and spacer implantation in a rat model.Bone Joint Res. 2022 Jun;11(6):371-385. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.116.BJR-2021-0319.R3. Bone Joint Res. 2022. PMID: 35708551 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol Reverses Thioacetamide-Induced Renal Assault with respect to Oxidative Stress, Renal Function, DNA Damage, and Cytokine Release in Wistar Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Sep 10;2019:1702959. doi: 10.1155/2019/1702959. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31583036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levine DP. Vancomycin: a history. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 42(Suppl 1): S5–S12. - PubMed
-
- Marre R, Schulz E, Anders T, Sack K. Renal tolerance and pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in rats. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984; 14: 253–260. - PubMed
-
- Nishino Y, Takemura S, Minamiyama Y, Hirohashi K, Ogino T, Inoue M, et al. Targeting superoxide dismutase to renal proximal tubule cells attenuates vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Free Radic Res. 2003; 37: 373–379. - PubMed
-
- Oktem F, Arslan MK, Ozguner F, Candir O, Yilmaz HR, Ciris M, et al. In vivo evidences suggesting the role of oxidative stress in pathogenesis of vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity: protection by erdosteine. Toxicology. 2005; 215: 227–233. - PubMed
-
- Appel GB, Given DB, Levine LR, Cooper GL. Vancomycin and the kidney. Am J Kidney Dis. 1986; 8: 75–78. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

