Co-evolving CENP-A and CAL1 Domains Mediate Centromeric CENP-A Deposition across Drosophila Species
- PMID: 27093083
- PMCID: PMC4861639
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.03.021
Co-evolving CENP-A and CAL1 Domains Mediate Centromeric CENP-A Deposition across Drosophila Species
Abstract
Centromeres mediate the conserved process of chromosome segregation, yet centromeric DNA and the centromeric histone, CENP-A, are rapidly evolving. The rapid evolution of Drosophila CENP-A loop 1 (L1) is thought to modulate the DNA-binding preferences of CENP-A to counteract centromere drive, the preferential transmission of chromosomes with expanded centromeric satellites. Consistent with this model, CENP-A from Drosophila bipectinata (bip) cannot localize to Drosophila melanogaster (mel) centromeres. We show that this result is due to the inability of the mel CENP-A chaperone, CAL1, to deposit bip CENP-A into chromatin. Co-expression of bip CENP-A and bip CAL1 in mel cells restores centromeric localization, and similar findings apply to other Drosophila species. We identify two co-evolving regions, CENP-A L1 and the CAL1 N terminus, as critical for lineage-specific CENP-A incorporation. Collectively, our data show that the rapid evolution of L1 modulates CAL1-mediated CENP-A assembly, suggesting an alternative mechanism for the suppression of centromere drive.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
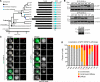
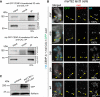

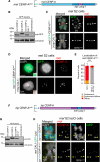
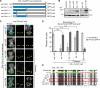
Comment in
-
Centromeres of a Different CAL-ibre.Dev Cell. 2016 Apr 18;37(2):105-6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.04.006. Dev Cell. 2016. PMID: 27093076
References
-
- Black BE, Foltz DR, Chakravarthy S, Luger K, Woods VL, Cleveland DW. Structural determinants for generating centromeric chromatin. Nature. 2004;430:578–582. - PubMed
-
- Camahort R, Li B, Florens L, Swanson SK, Washburn MP, Gerton JL. Scm3 is essential to recruit the histone H3 variant Cse4 to centromeres and to maintain a functional kinetochore. Mol. Cell. 2007;26:853–865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

