Weight and Glucose Reduction Observed with a Combination of Nutritional Agents in Rodent Models Does Not Translate to Humans in a Randomized Clinical Trial with Healthy Volunteers and Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 27093610
- PMCID: PMC4836696
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153151
Weight and Glucose Reduction Observed with a Combination of Nutritional Agents in Rodent Models Does Not Translate to Humans in a Randomized Clinical Trial with Healthy Volunteers and Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Background: Nutritional agents have modest efficacy in reducing weight and blood glucose in animal models and humans, but combinations are less well characterized. GSK2890457 (GSK457) is a combination of 4 nutritional agents, discovered by the systematic assessment of 16 potential components using the diet-induced obese mouse model, which was subsequently evaluated in a human study.
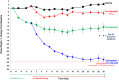
Nonclinical results: In the diet-induced obese mouse model, GSK457 (15% w/w in chow) given with a long-acting glucagon-like peptide -1 receptor agonist, exendin-4 AlbudAb, produced weight loss of 30.8% after 28 days of treatment. In db/db mice, a model of diabetes, GSK457 (10% w/w) combined with the exendin-4 AlbudAb reduced glucose by 217 mg/dL and HbA1c by 1.2% after 14 days.
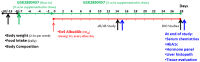
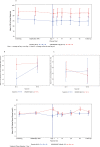
Clinical results: GSK457 was evaluated in a 6 week randomized, placebo-controlled study that enrolled healthy subjects and subjects with type 2 diabetes to investigate changes in weight and glucose. In healthy subjects, GSK457 well tolerated when titrated up to 40 g/day, and it reduced systemic exposure of metformin by ~ 30%. In subjects with diabetes taking liraglutide 1.8 mg/day, GSK457 did not reduce weight, but it slightly decreased mean glucose by 0.356 mmol/L (95% CI: -1.409, 0.698) and HbAlc by 0.065% (95% CI: -0.495, 0.365), compared to placebo. In subjects with diabetes taking metformin, weight increased in the GSK457-treated group [adjusted mean % increase from baseline: 1.26% (95% CI: -0.24, 2.75)], and mean glucose and HbA1c were decreased slightly compared to placebo [adjusted mean glucose change from baseline: -1.22 mmol/L (95% CI: -2.45, 0.01); adjusted mean HbA1c change from baseline: -0.219% (95% CI: -0.910, 0.472)].
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate remarkable effects of GSK457 in rodent models of obesity and diabetes, but a marked lack of translation to humans. Caution should be exercised with nutritional agents when predicting human efficacy from rodent models of obesity and diabetes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01725126.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
3 years of liraglutide versus placebo for type 2 diabetes risk reduction and weight management in individuals with prediabetes: a randomised, double-blind trial.Lancet. 2017 Apr 8;389(10077):1399-1409. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30069-7. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 28237263 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety over 26 weeks of an oral treatment strategy including sitagliptin compared with an injectable treatment strategy with liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin: a randomised clinical trial.Diabetologia. 2013 Jul;56(7):1503-11. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2905-1. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Diabetologia. 2013. PMID: 23604551 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised, placebo-controlled and active comparator-controlled phase 2 trial.Lancet. 2018 Nov 17;392(10160):2180-2193. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32260-8. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Lancet. 2018. PMID: 30293770 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term efficacy and safety comparison of liraglutide, glimepiride and placebo, all in combination with metformin in type 2 diabetes: 2-year results from the LEAD-2 study.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013 Mar;15(3):204-12. doi: 10.1111/dom.12012. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013. PMID: 22985213 Review.
-
Glycaemic efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors as add-on therapy to metformin in subjects with type 2 diabetes-a review and meta analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012 Aug;14(8):762-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2012.01603.x. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012. PMID: 22471248 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbiota and body weight control: Weight watchers within?Mol Metab. 2022 Mar;57:101427. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101427. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Mol Metab. 2022. PMID: 34973469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liraglutide-induced structural modulation of the gut microbiota in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.PeerJ. 2021 Apr 1;9:e11128. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11128. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33850659 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiome differences between metformin- and liraglutide-treated T2DM subjects.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2017 Dec 28;1(1):e00009. doi: 10.1002/edm2.9. eCollection 2018 Jan. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2017. PMID: 30815546 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Ketosis Affects Metabolism and Behavior in Sprague-Dawley Rats in Both Control and Chronic Stress Environments.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 May 15;10:129. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00129. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28555095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NIH Publication No. 98–4083. Health Risks of Overweight and Obesity. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults—The Evidence Report. Sep 1998: 12–25.
-
- Cani PD, Everard A, Duparc T. Gut microbiota, enteroendocrine functions and metabolism. Curt Opin Pharmacol. 2013;13;935–40. - PubMed
-
- Everard A, Cani PD, Diabetes, obesity, and gut microbiota. Best Prac Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;27(1):73–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

