Two Groups of Thellungiella salsuginea RAVs Exhibit Distinct Responses and Sensitivity to Salt and ABA in Transgenic Arabidopsis
- PMID: 27093611
- PMCID: PMC4836749
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153517
Two Groups of Thellungiella salsuginea RAVs Exhibit Distinct Responses and Sensitivity to Salt and ABA in Transgenic Arabidopsis
Abstract
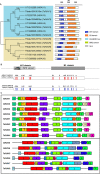
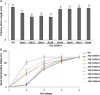
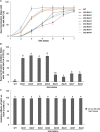
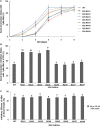
Containing both AP2 domain and B3 domain, RAV (Related to ABI3/VP1) transcription factors are involved in diverse functions in higher plants. A total of eight TsRAV genes were isolated from the genome of Thellungiella salsuginea and could be divided into two groups (A- and B-group) based on their sequence similarity. The mRNA abundance of all Thellungiella salsuginea TsRAVs followed a gradual decline during seed germination. In Thellungiella salsuginea seedling, transcripts of TsRAVs in the group A (A-TsRAVs) were gradually and moderately reduced by salt treatment but rapidly and severely repressed by ABA treatment. In comparison, with a barely detectable constitutive expression, the transcriptional level of TsRAVs in the group B (B-TsRAVs) exhibited a moderate induction in cotyledons when confronted with ABA. We then produced the "gain-of-function" transgenic Arabidopsis plants for each TsRAV gene and found that only 35S:A-TsRAVs showed weak growth retardation including reduced root elongation, suggesting their roles in negatively controlling plant growth. Under normal conditions, the germination process of all TsRAVs overexpressing transgenic seeds was inhibited with a stronger effect observed in 35S:A-TsRAVs seeds than in 35S:B-TsRAVs seeds. With the presence of NaCl, seed germination and seedling root elongation of all plants including wild type and 35S:TsRAVs plants were retarded and a more severe inhibition occurred to the 35S:A-TsRAV transgenic plants. ABA treatment only negatively affected the germination rates of 35S:A-TsRAV transgenic seeds but not those of 35S:B-TsRAV transgenic seeds. All 35S:TsRAVs transgenic plants showed a similar degree of reduction in root growth compared with untreated seedlings in the presence of ABA. Furthermore, the cotyledon greening/expansion was more severely inhibited 35S:A-TsRAVs than in 35S:B-TsRAVs seedlings. Upon water deficiency, with a wider opening of stomata, 35S:A-TsRAVs plants experienced a faster transpirational water loss than wild type and 35S:B-TsRAVs lines. Taken together, our results suggest that two groups of TsRAVs perform distinct regulating roles during plant growth and abiotic defense including drought and salt, and A-TsRAVs are more likely than B-TsRAVs to act as negative regulators in the above-mentioned biological processes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
A subset of Arabidopsis RAV transcription factors modulates drought and salt stress responses independent of ABA.Plant Cell Physiol. 2014 Nov;55(11):1892-904. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu118. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25189341
-
Functional Characterization of a Putative RNA Demethylase ALKBH6 in Arabidopsis Growth and Abiotic Stress Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 13;21(18):6707. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186707. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32933187 Free PMC article.
-
The maize WRKY transcription factor ZmWRKY17 negatively regulates salt stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants.Planta. 2017 Dec;246(6):1215-1231. doi: 10.1007/s00425-017-2766-9. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Planta. 2017. PMID: 28861611
-
Beyond Arabidopsis: BBX Regulators in Crop Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 12;22(6):2906. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062906. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33809370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LEAFY COTYLEDON 2: A Regulatory Factor of Plant Growth and Seed Development.Genes (Basel). 2021 Nov 26;12(12):1896. doi: 10.3390/genes12121896. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34946844 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SmRAV1, an AP2 and B3 Transcription Factor, Positively Regulates Eggplant's Response to Salt Stress.Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 15;12(24):4174. doi: 10.3390/plants12244174. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38140500 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of a Eutrema salsugineum phosphate transporter gene EsPHT1;4 enhances tolerance to low phosphorus stress in soybean.Biotechnol Lett. 2020 Nov;42(11):2425-2439. doi: 10.1007/s10529-020-02968-0. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Biotechnol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32683523
-
Two-State Co-Expression Network Analysis to Identify Genes Related to Salt Tolerance in Thai rice.Genes (Basel). 2018 Nov 29;9(12):594. doi: 10.3390/genes9120594. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30501128 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptative Mechanisms of Halophytic Eutrema salsugineum Encountering Saline Environment.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 28;13:909527. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.909527. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35837468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification of AP2/ERF superfamily genes and their expression during fruit ripening of Chinese jujube.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 23;8(1):15612. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33744-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30353116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McCarty DR, Hattori T, Carson CB, Vasil V, Lazar M, Vasil IK (1991) The Viviparous-1 developmental gene of maize encodes a novel transcriptional activator. Cell 66: 895–905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

