[Expression of microRNA-191 in T lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma and its underlying mechanism]
- PMID: 27093985
- PMCID: PMC7343091
- DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2016.04.003
[Expression of microRNA-191 in T lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma and its underlying mechanism]
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the correlation between MicroRNA-191 (miR-191) and T lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (T-ALL/LBL) to probe its underlying molecular mechanism.
Methods: The expression of miR-191 was examined by real-time PCR (RT-PCR) in 20 T-ALL/LBL tissue samples and 20 lymphoid reactive hyperplasia (LRH) tissue samples. The correlation between miR-191 and the clinicopathological feature of T-ALL/LBL was analyzed. Antisense miR-191 lentiviral vectors was constructed and transfected into T-ALL/LBL Jukat cells. After transfection, the expression of miR-191 was examined by RT-PCR. The cell activity was evaluated by CCK-8 asssy. The cell cycle and apoptosis were determined by flow cytometry.
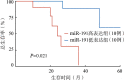
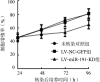
Results: Compared with LRH samples, the results of RT-PCR showed significant upregulation of miR-191 in 20 T-ALL/LBL tissue samples (1.875±0.079 vs 1.000, P<0.05). The expression level of miR-191 was negatively associated with prognosis. Compared with LV-NC-GFP and control groups, the expression of miR-191 significantly decreased after transfection of antisense miR-191 lentiviral vectors (0.578±0.012 vs 1.011±0.053 and 1.000, P<0.05), the percentages of apoptotic cells and the cell in G0/G1 phase significantly increased (P<0.05).
Conclusions: miR-191 might play a significant role in the development of T-ALL/LBL, implicating a new target for therapy.
目的: 探讨MicroRNA-191(miR-191)与T淋巴母细胞性白血病/淋巴瘤(T-ALL/LBL)的相关性及其作用机制。
方法: 采用荧光实时定量PCR(qRT-PCR)法检测20例T-ALL/LBL患者肿瘤组织和20例淋巴结反应性增生(LRH)患者淋巴结组织中miR-191的表达,并分析其与临床预后的关系。构建反义miR-191慢病毒载体(LV-miR-191-KD)和阴性对照载体(LV-NC-GFP)并转染T-ALL细胞系Jurkat细胞,qRT-PCR法检测miR-191的表达水平。分别用CCK-8法和流式细胞术检测下调miR-191后的细胞活性、细胞周期和凋亡。
结果: T-ALL/LBL患者组miR-191表达水平明显高于LRH患者组(1.875±0.079对1.000,P=0.001),以miR-191表达量的中位数为界,将T-ALL/LBL患者分为高表达组(10例)与低表达组(10例),高表达组患者3年OS率明显低于低表达组(26%对82%,P=0.021)。转染48 h后,LV-miR-191-KD组Jurkat细胞miR-191表达水平(0.578±0.012)较LV-NC-GFP组(1.011±0.053)和未转染对照组(1.000)显著降低(P值分别为0.018和0.021),细胞凋亡比例显著升高(P值均<0.05),细胞周期阻滞于G0/G1期,并抑制从G1期向S期转化。
结论: miR-191在T-ALL/LBL的发生、发展过程中起促进作用,可能作为T-ALL/LBL治疗的潜在靶点。
Figures
References
-
- Pui CH, Evans WE. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J] N Engl J Med. 2006;354(2):166–178. - PubMed