Rho/ROCK acts downstream of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 in modulating P2X3 receptor-mediated bone cancer pain in rats
- PMID: 27094551
- PMCID: PMC4956381
- DOI: 10.1177/1744806916644929
Rho/ROCK acts downstream of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 in modulating P2X3 receptor-mediated bone cancer pain in rats
Abstract
Background: Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 and Rho/ROCK signaling is implicated in bone cancer pain development. However, it remains unknown whether the two signaling pathways function together in P2X3 receptor-mediated bone cancer pain.
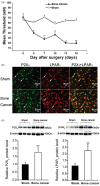
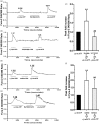
Results: In this study, using a rat model of bone cancer, we examined the expression of P2X3 and lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons and further dissected whether lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 and Rho/ROCK-mediated pathways interacted in modulating rat pain behavior. Bone cancer was established by inoculating Walker 256 cells into the left tibia of female Wistar rats. We observed a gradual and yet significant decline in mean paw withdrawal threshold in rats with bone cancer, but not in control rats. Our immunohistochemical staining revealed that the number of P2X3- and lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1-positive dorsal root ganglion neurons was significantly greater in rats with bone cancer than control rats. Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 blockade with VPC32183 significantly attenuated decline in mean paw withdrawal threshold. Flinching behavior test further showed that lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 inhibition with VPC32183 transiently but significantly attenuated α,β-meATP-induced increase in paw lift time per minute. Rho inhibition by intrathecal BoTXC3 caused a rapid reversal in decline in mean paw withdrawal threshold of rats with bone cancer. Flinching behavior test showed that BoTXC3 transiently and significantly attenuated α,β-meATP-induced increase in paw lift time per minute. Similar findings were observed with ROCK inhibition by intrathecal Y27632. Furthermore, VPC32183 and BoTXC3 effectively aborted the appearance of lysophosphatidic acid-induced calcium influx peak.
Conclusions: Lysophosphatidic acid and its receptor LPAR1, acting through the Rho-ROCK pathway, regulate P2X3 receptor in the development of both mechanical and spontaneous pain in bone cancer.
Keywords: Bone cancer pain; P2X3 receptor; Rho/ROCK; lysophosphatidic acid receptor.
© The Author(s) 2016.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on bone cancer pain in rat model: the role of peripheral P2X3 receptor.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Mar;19(1):13-27. doi: 10.1007/s11302-022-09861-7. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 35478452 Free PMC article.
-
Functional up-regulation of P2X3 receptors in dorsal root ganglion in a rat model of bone cancer pain.Eur J Pain. 2012 Nov;16(10):1378-88. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2012.00149.x. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Eur J Pain. 2012. PMID: 22528605
-
Potentiation of P2X3 receptor mediated currents by endothelin-1 in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Dec 15;181:108356. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108356. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 33069757
-
Group II metabotropic glutamate receptor activation suppresses ATP currents in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons.Neuropharmacology. 2023 Apr 1;227:109443. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109443. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Neuropharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36709909 Review.
-
P2X3 receptors are transducers of sensory signals.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Sep;151:119-124. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.12.020. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30660716 Review.
Cited by
-
Analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on bone cancer pain in rat model: the role of peripheral P2X3 receptor.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Mar;19(1):13-27. doi: 10.1007/s11302-022-09861-7. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 35478452 Free PMC article.
-
P2X receptor channels in chronic pain pathways.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;175(12):2219-2230. doi: 10.1111/bph.13957. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28728214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of P2X3 Receptor-Mediated Currents by Lysophosphatidic Acid in Rat Primary Sensory Neurons.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 20;13:928647. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.928647. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35795546 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic Acid and Ion Channels as Molecular Mediators of Pain.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Dec 12;11:462. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00462. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30618613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNA-329 reduces bone cancer pain through the LPAR1-dependent LPAR1/ERK signal transduction pathway in mice.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2019 Oct 23;11:1758835919875319. doi: 10.1177/1758835919875319. eCollection 2019. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31692673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sabino MA, Mantyh PW. Pathophysiology of bone cancer pain. J Support Oncol 2005; 3: 15–24. - PubMed
-
- Guo G, Gao F. CXCR3: latest evidence for the involvement of chemokine signaling in bone cancer pain. Exp Neurol 2015; 265: 176–179. - PubMed
-
- Hu XM, Liu YN, Zhang HL, et al. CXCL12/CXCR4 chemokine signaling in spinal glia induces pain hypersensitivity through MAPKs-mediated neuroinflammation in bone cancer rats. J Neurochem 2015; 132: 452–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

