Sphingosine 1-phosphate elicits RhoA-dependent proliferation and MRTF-A mediated gene induction in CPCs
- PMID: 27094722
- PMCID: PMC5004781
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.04.006
Sphingosine 1-phosphate elicits RhoA-dependent proliferation and MRTF-A mediated gene induction in CPCs
Abstract
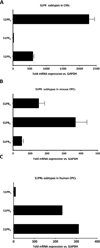
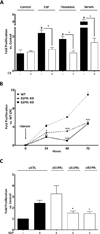
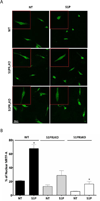
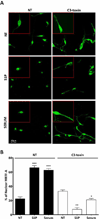
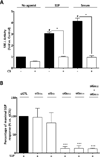
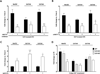
Although c-kit(+) cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs) are currently used in clinical trials there remain considerable gaps in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying their proliferation and differentiation. G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) play an important role in regulating these processes in mammalian cell types thus we assessed GPCR mRNA expression in c-kit(+) cells isolated from adult mouse hearts. Our data provide the first comprehensive overview of the distribution of this fundamental class of cardiac receptors in CPCs and reveal notable distinctions from that of adult cardiomyocytes. We focused on GPCRs that couple to RhoA activation in particular those for sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). The S1P2 and S1P3 receptors are the most abundant S1P receptor subtypes in mouse and human CPCs while cardiomyocytes express predominantly S1P1 receptors. Treatment of CPCs with S1P, as with thrombin and serum, increased proliferation through a pathway requiring RhoA signaling, as evidenced by significant attenuation when Rho was inhibited by treatment with C3 toxin. Further analysis demonstrated that both S1P- and serum-induced proliferation are regulated through the S1P2 and S1P3 receptor subtypes which couple to Gα12/13 to elicit RhoA activation. The transcriptional co-activator MRTF-A was activated by S1P as assessed by its nuclear accumulation and induction of a RhoA/MRTF-A luciferase reporter. In addition S1P treatment increased expression of cardiac lineage markers Mef2C and GATA4 and the smooth muscle marker GATA6 through activation of MRTF-A. In conclusion, we delineate an S1P-regulated signaling pathway in CPCs that introduces the possibility of targeting S1P2/3 receptors, Gα12/13 or RhoA to influence the proliferation and commitment of c-kit(+) CPCs and improve the response of the myocardium following injury.
Keywords: Cardiac progenitor cells; GPCR; MRTF-A; RhoA; Sphingosine-1-phosphate.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate stimulates smooth muscle cell differentiation and proliferation by activating separate serum response factor co-factors.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 8;279(41):42422-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405432200. Epub 2004 Aug 3. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15292266
-
Induction of the matricellular protein CCN1 through RhoA and MRTF-A contributes to ischemic cardioprotection.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Oct;75:152-61. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.07.017. Epub 2014 Aug 8. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25106095 Free PMC article.
-
Selective coupling of the S1P3 receptor subtype to S1P-mediated RhoA activation and cardioprotection.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017 Feb;103:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.12.008. Epub 2016 Dec 23. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28017639 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and biological activities in the cardiovascular system.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Sep;1781(9):483-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.04.003. Epub 2008 Apr 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18472021 Review.
-
Vascular sphingosine-1-phosphate S1P1 and S1P3 receptors.Drug News Perspect. 2004 Jul-Aug;17(6):365-82. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2004.17.6.829028. Drug News Perspect. 2004. PMID: 15334188 Review.
Cited by
-
Adult Cardiac Stem Cell Aging: A Reversible Stochastic Phenomenon?Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Feb 7;2019:5813147. doi: 10.1155/2019/5813147. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 30881594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) signaling on excessive stress-induced root resorption during orthodontic molar intrusion.Clin Oral Investig. 2022 Jan;26(1):1003-1016. doi: 10.1007/s00784-021-04084-3. Epub 2021 Aug 7. Clin Oral Investig. 2022. PMID: 34363103
-
Gα12 and Gα13: Versatility in Physiology and Pathology.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 14;10:809425. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.809425. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35237598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expansion of Sphingosine Kinase and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor Function in Normal and Cancer Cells: From Membrane Restructuring to Mediation of Estrogen Signaling and Stem Cell Programming.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 31;19(2):420. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020420. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29385066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RhoA regulates Drp1 mediated mitochondrial fission through ROCK to protect cardiomyocytes.Cell Signal. 2018 Oct;50:48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.06.012. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 29953931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferrari R, Ceconi C, Campo G, et al. Mechanisms of remodelling: a question of life (stem cell production) and death (myocyte apoptosis) Circ J. 2009;73:1973–1982. - PubMed
-
- Piccoli MT, Gupta SK, Thum T. Noncoding RNAs as regulators of cardiomyocyte proliferation and death. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015 - PubMed
-
- Fuster JJ, Andres V. Telomere biology and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2006;99:1167–1180. - PubMed
-
- Beltrami AP, Urbanek K, Kajstura J, et al. Evidence that human cardiac myocytes divide after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1750–1757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

