Hypoxia-inducible factors as molecular targets for liver diseases
- PMID: 27094811
- PMCID: PMC4879168
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-016-1408-1
Hypoxia-inducible factors as molecular targets for liver diseases
Abstract
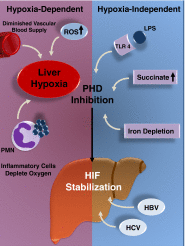
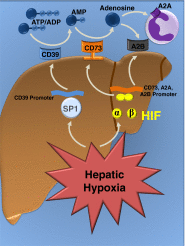
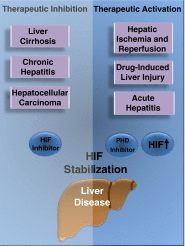
Liver disease is a growing global health problem, as deaths from end-stage liver cirrhosis and cancer are rising across the world. At present, pharmacologic approaches to effectively treat or prevent liver disease are extremely limited. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) is a transcription factor that regulates diverse signaling pathways enabling adaptive cellular responses to perturbations of the tissue microenvironment. HIF activation through hypoxia-dependent and hypoxia-independent signals have been reported in liver disease of diverse etiologies, from ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute liver injury to chronic liver diseases caused by viral infection, excessive alcohol consumption, or metabolic disorders. This review summarizes the evidence for HIF stabilization in liver disease, discusses the mechanistic involvement of HIFs in disease development, and explores the potential of pharmacological HIF modifiers in the treatment of liver disease.
Keywords: Alcoholic liver disease; Fatty liver; HIF1α; HIF2α; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Ischemia-reperfusion liver injury; Viral hepatitis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AA022387/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL114457/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL098294/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA021723/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103712/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002182/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 DK097075/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK095491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092188/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL119837/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK104713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

