Resequencing analysis of five Mendelian genes and the top genes from genome-wide association studies in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 27094865
- PMCID: PMC4837564
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-016-0097-0
Resequencing analysis of five Mendelian genes and the top genes from genome-wide association studies in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
Background: Most sequencing studies in Parkinson's disease (PD) have focused on either a particular gene, primarily in familial and early onset PD samples, or on screening single variants in sporadic PD cases. To date, there is no systematic study that sequences the most common PD causing genes with Mendelian inheritance [α-synuclein (SNCA), leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2), PARKIN, PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1) and DJ-1 (Daisuke-Junko-1)] and susceptibility genes [glucocerebrosidase beta acid (GBA) and microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT)] identified through genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in a European-American case-control sample (n=815).
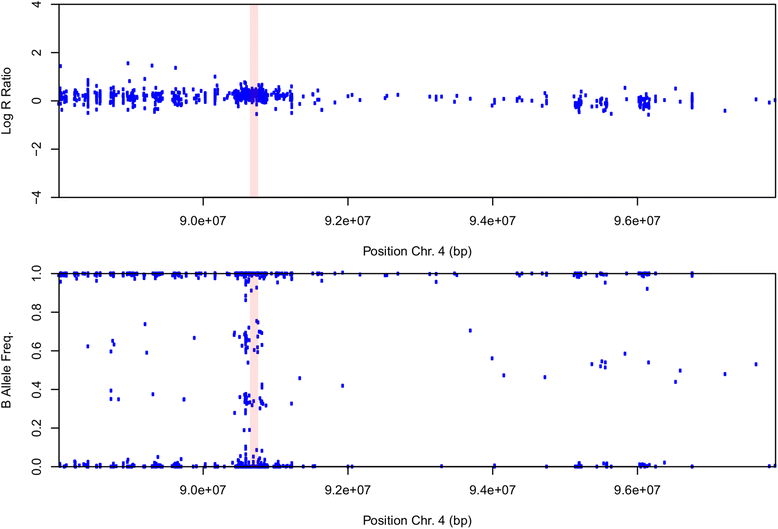
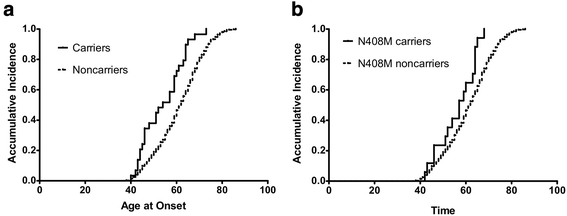
Results: Disease-causing variants in the SNCA, LRRK2 and PARK2 genes were found in 2% of PD patients. The LRRK2, p.G2019S mutation was found in 0.6 % of sporadic PD and 4.8 % of familial PD cases. Gene-based analysis suggests that additional variants in the LRRK2 gene also contribute to PD risk. The SNCA duplication was found in 0.8 % of familial PD patients. Novel variants were found in 0.8% of PD cases and 0.6 % of controls. Heterozygous Gaucher disease-causing mutations in the GBA gene were found in 7.1 % of PD patients. Here, we established that the GBA variant (p.T408M) is associated with PD risk and age at onset. Additionally, gene-based and single-variant analyses demostrated that GBA gene variants (p.L483P, p.R83C, p.N409S, p.H294Q and p.E365K) increase PD risk.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that the impact of additional untested coding variants in the GBA and LRRK2 genes is higher than previously estimated. Our data also provide compelling evidence of the existence of additional untested variants in the primary Mendelian and PD GWAS genes that contribute to the genetic etiology of sporadic PD.
Keywords: Association study; DJ-1; GBA rare variants, gene-based analysis; LRRK2; MAPT; PARKIN; PINK1; Parkinson’s; SNCA.
Figures
References
-
- Dorsey ER, Constantinescu R, Thompson JP, Biglan KM, Holloway RG, Kieburtz K, Marshall FJ, Ravina BM, Schifitto G, Siderowf A, Tanner CM. Projected number of people with Parkinson disease in the most populous nations, 2005 through 2030. Neurology. 2007;68:384–6. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000247740.47667.03. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sharma M, Ioannidis JPA, Aasly JO, Annesi G, Brice A, Van Broeckhoven C, Bertram L, Bozi M, Crosiers D, Clarke C, Facheris M, Farrer M, Garraux G, Gispert S, Auburger G, Vilariño-Güell C, Hadjigeorgiou GM, Hicks AA, Hattori N, Jeon B, Lesage S, Lill CM, Lin JJ, Lynch T, Lichtner P, Lang AE, Mok V, Jasinska-Myga B, Mellick GD, Morrison KE, et al. Large-scale replication and heterogeneity in Parkinson disease genetic loci. Neurology. 2012;79:659–67. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318264e353. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nalls MA, Pankratz N, Lill CM, Do CB, Hernandez DG, Saad M, DeStefano AL, Kara E, Bras J, Sharma M, Schulte C, Keller MF, Arepalli S, Letson C, Edsall C, Stefansson H, Liu X, Pliner H, Lee JH, Cheng R, International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics C, Parkinson’s Study Group Parkinson's Research: The Organized GenI, andMe, GenePd, NeuroGenetics Research C, Hussman Institute of Human G, Ashkenazi Jewish Dataset I, Cohorts for H, Aging Research in Genetic E, North American Brain Expression C et al. Large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies six new risk loci for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet. 2014;46:989–93. doi: 10.1038/ng.3043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

