A 10-year study reveals clinical and laboratory evidence for the 'semi-invasive' properties of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis
- PMID: 27094904
- PMCID: PMC4855073
- DOI: 10.1038/emi.2016.31
A 10-year study reveals clinical and laboratory evidence for the 'semi-invasive' properties of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis
Abstract
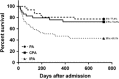
In recent years, infections caused by Aspergillus sp. have become an emerging focus of clinical microbiology and infectious disease, as the number of patients infected with Aspergillus sp. has increased markedly. Although chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA) is considered a 'semi-invasive' or 'intermediate' disease, little data are available for the direct comparison of CPA with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) and pulmonary aspergilloma (PA) to quantify invasiveness. In this study, we compared the characteristics of CPA with those of IPA and PA among hospitalized patients over a 10-year period. A total of 29, 51 and 31 cases of CPA, IPA and PA, respectively, were included. An increasing trend in galactomannan antigen seropositivity rate from PA (24.1%) to CPA (35.7%) to IPA (54.9%) and an opposite trend for anti-Aspergillus antibody (PA (71.0%) to CPA (45.8%) to IPA (7.1%)) were observed. Eight percent of CPA patients were infected with more than one Aspergillus sp. The survival rate of the CPA group also fell between the survival rate of PA and IPA, confirming the intermediate severity of CPA. The survival rate of the CPA group became significantly higher than that of the IPA group from day 180 onwards until 2 years after admission (P<0.05). The survival rate of the CPA group remained lower than that of the PA group from day 30 onwards until 2 years after admission. Poor prognostic factors for CPA included older age (P=0.019), higher total leukocyte count (P=0.011) and higher neutrophil count (P=0.012) on admission. This study provided clinical and laboratory evidence for the semi-invasive properties of CPA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical characteristics and prognosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis.Respir Med. 2012 May;106(5):724-9. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2012.01.014. Epub 2012 Feb 19. Respir Med. 2012. PMID: 22349065
-
Potential value of serum Aspergillus IgG antibody detection in the diagnosis of invasive and chronic pulmonary aspergillosis in non-agranulocytic patients.BMC Pulm Med. 2020 Apr 15;20(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-1125-y. BMC Pulm Med. 2020. PMID: 32293386 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Aspergillus-Specific Lateral-Flow Device Test Using Serum and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid for Diagnosis of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis.J Clin Microbiol. 2019 Apr 26;57(5):e00095-19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00095-19. Print 2019 May. J Clin Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30842231 Free PMC article.
-
The spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis.Respir Med. 2018 Aug;141:121-131. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2018.06.029. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Respir Med. 2018. PMID: 30053957 Review.
-
[Aspergillus in airway material : Ignore or treat?].Internist (Berl). 2017 Nov;58(11):1150-1162. doi: 10.1007/s00108-017-0334-9. Internist (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28986661 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Clinical and Microbiological Characteristics of Aspergillosis at a Chinese Tertiary Teaching Hospital.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Dec 11;15:7249-7257. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S391069. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36533254 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review to Assess the Relationship between Disseminated Cerebral Aspergillosis, Leukemias and Lymphomas, and Their Respective Therapeutics.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Jul 11;8(7):722. doi: 10.3390/jof8070722. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35887477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic factors of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: A retrospective cohort of 264 patients from Japan.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 1;16(4):e0249455. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249455. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33793645 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis: Notes for a Clinician in a Resource-Limited Setting Where There Is No Mycologist.J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Jun 2;6(2):75. doi: 10.3390/jof6020075. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32498415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Gβ-like Protein AfCpcB Affects Sexual Development, Response to Oxidative Stress and Phagocytosis by Alveolar Macrophages in Aspergillus fumigatus.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Jan 6;8(1):56. doi: 10.3390/jof8010056. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35049996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yuen KY, Woo PC, Ip MS et al. Stage-specific manifestation of mold infections in bone marrow transplant recipients: risk factors and clinical significance of positive concentrated smears. Clin Infect Dis 1997; 25: 37–42. - PubMed
-
- Gefter WB, Weingrad TR, Epstein DM, Ochs RH, Miller WT. ‘Semi-invasive' pulmonary aspergillosis: a new look at the spectrum of aspergillus infections of the lung. Radiology 1981; 140: 313–321. - PubMed
-
- Binder RE, Faling LJ, Pugatch RD, Mahasaen C, Snider GL. Chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis: a discrete clinical entity. Medicine 1982; 61: 109–124. - PubMed
-
- Denning DW, Riniotis K, Dobrashian R, Sambatakou H. Chronic cavitary and fibrosing pulmonary and pleural aspergillosis: case series, proposed nomenclature change, and review. Clin Infect Dis 2003; 37 (Suppl 3): S265–S280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
