Disruption of corticocortical information transfer during ketamine anesthesia in the primate brain
- PMID: 27095309
- PMCID: PMC4912854
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.04.039
Disruption of corticocortical information transfer during ketamine anesthesia in the primate brain
Abstract
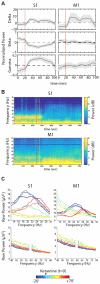
The neural mechanisms of anesthetic-induced unconsciousness have yet to be fully elucidated, in part because of the diverse molecular targets of anesthetic agents. We demonstrate, using intracortical recordings in macaque monkeys, that information transfer between structurally connected cortical regions is disrupted during ketamine anesthesia, despite preserved primary sensory representation. Furthermore, transfer entropy, an information-theoretic measure of directed connectivity, decreases significantly between neuronal units in the anesthetized state. This is the first direct demonstration of a general anesthetic disrupting corticocortical information transfer in the primate brain. Given past studies showing that more commonly used GABAergic drugs inhibit surrogate measures of cortical communication, this finding suggests the potential for a common network-level mechanism of anesthetic-induced unconsciousness.
Keywords: Anesthesia; Consciousness; Functional connectivity; Information integration; Ketamine; Sensorimotor.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Antkowiak B. Different actions of general anesthetics on the firing patterns of neocortical neurons mediated by the GABA(A) receptor. Anesthesiology. 1999;91:500–511. - PubMed
-
- Banoub M, Tetzlaff JE, Schubert A. Pharmacologic and physiologic influences affecting sensory evoked potentials: implications for perioperative monitoring. Anesthesiology. 2003;99:716–737. - PubMed
-
- Boveroux P, Vanhaudenhuyse A, Bruno M-A, Noirhomme Q, Lauwick S, Luxen A, Degueldre C, Plenevaux A, Schnakers C, Phillips C, Brichant J-F, Bonhomme V, Maquet P, Greicius MD, Laureys S, Boly M. Breakdown of within- and between-network resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging connectivity during propofol-induced loss of consciousness. Anesthesiology. 2010;113:1038–1053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
