Protective effect of bioactive compounds from Lonicera japonica Thunb. against H2O2-induced cytotoxicity using neonatal rat cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 27096070
- PMCID: PMC4823622
Protective effect of bioactive compounds from Lonicera japonica Thunb. against H2O2-induced cytotoxicity using neonatal rat cardiomyocytes
Abstract
Objectives: Pharmacological studies showed that the extracts of Jin Yin Hua and its active constituents have lipid lowering, antipyretic, hepatoprotective, cytoprotective, antimicrobial, antibiotic, antioxidative, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory effects. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the protective effects of caffeoylquinic acids (CQAs) from Jin Yin Hua against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced and hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity using neonatal rat cardiomyocytes.
Materials and methods: Seven CQAs (C1 to C7) isolated and identified from Jin Yin Hua were used to examine the effects of H2O2-induced and hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity. We studied C4 and C6 as preventative bioactive compounds of the reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, apoptotic pathway, and apoptosis-related gene expression.
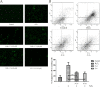
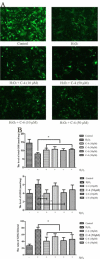
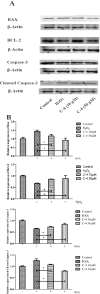
Results: C4 and C6 were screened as bioactive compounds to exert a cytoprotective effect against oxidative injury. Pretreatment with C4 and C6, dose-dependently attenuated hypoxia-induced ROS production and reduced the ratio of GSSG/GStotal. Western blot data revealed that the inhibitory effect of C4 on H2O2-induced up and down-regulation of Bcl-2, Bax, caspase-3, and cleaved caspase-3. Apoptosis was evaluated by detection of DNA fragmentation using TUNEL assay, and quantified with Annexin V/PI staining.
Conclusion: In vitro experiments revealed that both C4 and C6 protect cardiomyocytes from necrosis and apoptosis during H2O2-induced injury, via inhibiting the generation of ROS and activation of caspase-3 apoptotic pathway. These results demonstrated that CQAs might be a class of compounds which possess potent myocardial protective activity against the ischemic heart diseases related to oxidative stress.
Keywords: Anti-apoptosis; Caffeoylquinic acids; Cardiomyocytes; Lonicera japonica Thunb; Oxidative stress.
Figures


References
-
- Hayes O. Fact sheet: cardiovascular disease (ICD-9 390-448) and women. Chronic Dis Can. 1996;17:28–30. - PubMed
-
- Sun HY, Wang NP, Kerendi F, Halkos M, Kin H, Guyton RA, et al. Hypoxic postconditioning reduces cardiomyocyte loss by inhibiting ROS generation and intracellular Ca2+ overload. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H1900–908. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
