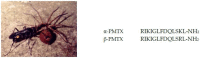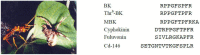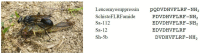Peptide Toxins in Solitary Wasp Venoms
- PMID: 27096870
- PMCID: PMC4848640
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins8040114
Peptide Toxins in Solitary Wasp Venoms
Abstract
Solitary wasps paralyze insects or spiders with stinging venom and feed the paralyzed preys to their larva. Accordingly, the venoms should contain a variety of constituents acting on nervous systems. However, only a few solitary wasp venoms have been chemically studied despite thousands of species inhabiting the planet. We have surveyed bioactive substances in solitary wasp venoms found in Japan and discovered a variety of novel bioactive peptides. Pompilidotoxins (PMTXs), in the venoms of the pompilid wasps Anoplius samariensis and Batozonellus maculifrons, are small peptides consisting of 13 amino acids without a disulfide bond. PMTXs slowed Na⁺ channel inactivation, in particular against neuronal type Na⁺ channels, and were rather selective to the Nav1.6 channel. Mastoparan-like cytolytic and antimicrobial peptides are the major components of eumenine wasp venoms. They are rich in hydrophobic and basic amino acids, adopting a α-helical secondary structure, and showing mast cell degranulating, antimicrobial and hemolytic activities. The venom of the spider wasp Cyphononyx fulvognathus contained four bradykinin-related peptides. They are hyperalgesic and, dependent on the structure, differently associated with B₁ or B₂ receptors. Further survey led to the isolation of leucomyosuppressin-like FMRFamide peptides from the venoms of the digger wasps Sphex argentatus and Isodontia harmandi. These results of peptide toxins in solitary wasp venoms from our studies are summarized.
Keywords: FMRFamide neuropeptide; bradykinin-related peptide; cytolytic peptide; neurotoxin; peptide toxin; solitary wasp.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemical and Biological Characteristics of Antimicrobial α-Helical Peptides Found in Solitary Wasp Venoms and Their Interactions with Model Membranes.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Sep 24;11(10):559. doi: 10.3390/toxins11100559. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31554187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Analysis and Biological Characterization of Venom Components from Solitary Scoliid Wasp Campsomeriella annulata annulata.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Dec 10;13(12):885. doi: 10.3390/toxins13120885. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34941722 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and structure of pompilidotoxins, novel peptide neurotoxins in solitary wasp venoms.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Sep 29;250(3):612-6. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.9299. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998. PMID: 9784394
-
Isolation and characterization of FMRFamide-like peptides in the venoms of solitary sphecid wasps.Peptides. 2021 Aug;142:170575. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2021.170575. Epub 2021 May 20. Peptides. 2021. PMID: 34023397
-
Differential Properties of Venom Peptides and Proteins in Solitary vs. Social Hunting Wasps.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Jan 22;8(2):32. doi: 10.3390/toxins8020032. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 26805885 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Short Review of the Venoms and Toxins of Spider Wasps (Hymenoptera: Pompilidae).Toxins (Basel). 2021 Oct 21;13(11):744. doi: 10.3390/toxins13110744. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34822528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical manifestations of wasp stings: a case report and a review of literature.Trop Med Health. 2022 Oct 28;50(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s41182-022-00475-8. Trop Med Health. 2022. PMID: 36307881 Free PMC article.
-
Sa12b Peptide from Solitary Wasp Inhibits ASIC Currents in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Oct 10;11(10):585. doi: 10.3390/toxins11100585. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31658776 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-Tuning of Alkaline Residues on the Hydrophilic Face Provides a Non-toxic Cationic α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptide Against Antibiotic-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jul 15;12:684591. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.684591. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34335511 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidomic analysis of the venom of the solitary bee Xylocopa appendiculata circumvolans.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2017 Aug 29;23:40. doi: 10.1186/s40409-017-0130-y. eCollection 2017. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 28855917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banks B.E.C., Shipolini R.A. Chemistry and pharmacology of honey-bee venom. In: Piek T., editor. Venoms of the Hymenoptera: Biochemical, Pharmacological and Behavioural Aspects. Academic Press; London, UK: 1986. pp. 330–416.
-
- Nakajima T. Pharmacological biochemistry of vespid venoms. In: Piek T., editor. Venoms of the Hymenoptera: Biochemical, Pharmacological and Behavioural Aspects. Academic Press; London, UK: 1986. pp. 309–327.
-
- Piek T., Spanjer W. Chemistry and pharmacology of solitary wasp venoms. In: Piek T., editor. Venoms of the Hymenoptera: Biochemical, Pharmacological and Behavioural Aspects. Academic Press; London, UK: 1986. pp. 161–307.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources