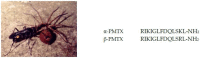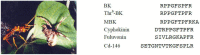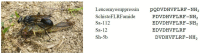Peptide Toxins in Solitary Wasp Venoms
- PMID: 27096870
- PMCID: PMC4848640
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins8040114
Peptide Toxins in Solitary Wasp Venoms
Abstract
Solitary wasps paralyze insects or spiders with stinging venom and feed the paralyzed preys to their larva. Accordingly, the venoms should contain a variety of constituents acting on nervous systems. However, only a few solitary wasp venoms have been chemically studied despite thousands of species inhabiting the planet. We have surveyed bioactive substances in solitary wasp venoms found in Japan and discovered a variety of novel bioactive peptides. Pompilidotoxins (PMTXs), in the venoms of the pompilid wasps Anoplius samariensis and Batozonellus maculifrons, are small peptides consisting of 13 amino acids without a disulfide bond. PMTXs slowed Na⁺ channel inactivation, in particular against neuronal type Na⁺ channels, and were rather selective to the Nav1.6 channel. Mastoparan-like cytolytic and antimicrobial peptides are the major components of eumenine wasp venoms. They are rich in hydrophobic and basic amino acids, adopting a α-helical secondary structure, and showing mast cell degranulating, antimicrobial and hemolytic activities. The venom of the spider wasp Cyphononyx fulvognathus contained four bradykinin-related peptides. They are hyperalgesic and, dependent on the structure, differently associated with B₁ or B₂ receptors. Further survey led to the isolation of leucomyosuppressin-like FMRFamide peptides from the venoms of the digger wasps Sphex argentatus and Isodontia harmandi. These results of peptide toxins in solitary wasp venoms from our studies are summarized.
Keywords: FMRFamide neuropeptide; bradykinin-related peptide; cytolytic peptide; neurotoxin; peptide toxin; solitary wasp.
Figures
References
-
- Banks B.E.C., Shipolini R.A. Chemistry and pharmacology of honey-bee venom. In: Piek T., editor. Venoms of the Hymenoptera: Biochemical, Pharmacological and Behavioural Aspects. Academic Press; London, UK: 1986. pp. 330–416.
-
- Nakajima T. Pharmacological biochemistry of vespid venoms. In: Piek T., editor. Venoms of the Hymenoptera: Biochemical, Pharmacological and Behavioural Aspects. Academic Press; London, UK: 1986. pp. 309–327.
-
- Piek T., Spanjer W. Chemistry and pharmacology of solitary wasp venoms. In: Piek T., editor. Venoms of the Hymenoptera: Biochemical, Pharmacological and Behavioural Aspects. Academic Press; London, UK: 1986. pp. 161–307.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources