Language and thought are not the same thing: evidence from neuroimaging and neurological patients
- PMID: 27096882
- PMCID: PMC4874898
- DOI: 10.1111/nyas.13046
Language and thought are not the same thing: evidence from neuroimaging and neurological patients
Abstract
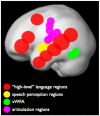
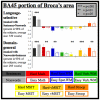
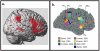
Is thought possible without language? Individuals with global aphasia, who have almost no ability to understand or produce language, provide a powerful opportunity to find out. Surprisingly, despite their near-total loss of language, these individuals are nonetheless able to add and subtract, solve logic problems, think about another person's thoughts, appreciate music, and successfully navigate their environments. Further, neuroimaging studies show that healthy adults strongly engage the brain's language areas when they understand a sentence, but not when they perform other nonlinguistic tasks such as arithmetic, storing information in working memory, inhibiting prepotent responses, or listening to music. Together, these two complementary lines of evidence provide a clear answer: many aspects of thought engage distinct brain regions from, and do not depend on, language.
Keywords: aphasia; cognitive control; executive functions; fMRI; functional specificity; language; music; navigation; neuropsychology; numerical cognition; semantics; syntax; theory of mind.
© 2016 New York Academy of Sciences.
Figures

References
-
- The Guardian [Accessed February 15, 2016];Tom Lubbock: a memoir of living with a brain tumour. 2016 Nov 6; 2010. http://www.theguardian.com/books/2010/nov/07/tom-lubbock-brain-tumour-la....
-
- Call J. Chimpanzee social cognition. Trends In Cogn. Sci. 2001;5:388–393. - PubMed
-
- Tomasello M, Call J, Hare B. Chimpanzees understand psychological states - the question is which ones and to what extent. Trends In Cogn. Sci. 2003;7:153–156. - PubMed
-
- Hurley S, Nudds M. Rational Animals? Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 2006.
-
- Penn D, Povinelli D. Causal Cognition in Human and Nonhuman Animals: A Comparative, Critical Review. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2007;58:97–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

