New Cysteine-Rich Ice-Binding Protein Secreted from Antarctic Microalga, Chloromonas sp
- PMID: 27097164
- PMCID: PMC4838330
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154056
New Cysteine-Rich Ice-Binding Protein Secreted from Antarctic Microalga, Chloromonas sp
Abstract
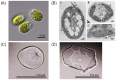
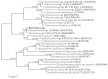
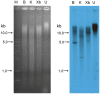
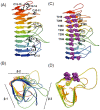
Many microorganisms in Antarctica survive in the cold environment there by producing ice-binding proteins (IBPs) to control the growth of ice around them. An IBP from the Antarctic freshwater microalga, Chloromonas sp., was identified and characterized. The length of the Chloromonas sp. IBP (ChloroIBP) gene was 3.2 kb with 12 exons, and the molecular weight of the protein deduced from the ChloroIBP cDNA was 34.0 kDa. Expression of the ChloroIBP gene was up- and down-regulated by freezing and warming conditions, respectively. Western blot analysis revealed that native ChloroIBP was secreted into the culture medium. This protein has fifteen cysteines and is extensively disulfide bonded as shown by in-gel mobility shifts between oxidizing and reducing conditions. The open-reading frame of ChloroIBP was cloned and over-expressed in Escherichia coli to investigate the IBP's biochemical characteristics. Recombinant ChloroIBP produced as a fusion protein with thioredoxin was purified by affinity chromatography and formed single ice crystals of a dendritic shape with a thermal hysteresis activity of 0.4±0.02°C at a concentration of 5 mg/ml. In silico structural modeling indicated that the three-dimensional structure of ChloroIBP was that of a right-handed β-helix. Site-directed mutagenesis of ChloroIBP showed that a conserved region of six parallel T-X-T motifs on the β-2 face was the ice-binding region, as predicted from the model. In addition to disulfide bonding, hydrophobic interactions between inward-pointing residues on the β-1 and β-2 faces, in the region of ice-binding motifs, were crucial to maintaining the structural conformation of ice-binding site and the ice-binding activity of ChloroIBP.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures









References
-
- Priddle J, Hawes I, Ellis-Evans JC. Antarctic aquatic ecosystems as habitats for phytoplankton. Biol Rev. 1986; 61(3):199–238.
-
- Ehn JK, Mundy CJ. Assessment of light absorption within highly scattering bottom sea ice from under-ice light measurements: Implications for Arctic ice algae primary production. Limnol Oceanogr. 2013; 58(3):893–902.
-
- Thomas DN, Dieckmann GS. Antarctic sea ice-a habitat for extremophiles. Science. 2002; 295(5555):641–4. - PubMed
-
- Mock T, Thomas DN. Recent advances in sea-ice microbiology. Environ Microbiol. 2005; 7(5):605–19. - PubMed
-
- Eicken H, Bock C, Wittig R, Miller H, Poertner HO. Magnetic resonance imaging of sea-ice pore fluids: methods and thermal evolution of pore microstructure. Cold Reg Sci Technol. 2000; 31(3):207–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

