Effectiveness of Multiple Blood-Cleansing Interventions in Sepsis, Characterized in Rats
- PMID: 27097769
- PMCID: PMC4838820
- DOI: 10.1038/srep24719
Effectiveness of Multiple Blood-Cleansing Interventions in Sepsis, Characterized in Rats
Abstract
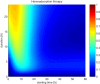
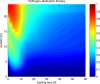
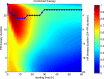
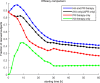
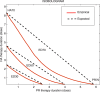
Sepsis is a serious, life-threatening condition that presents a growing problem in medicine, but there is still no satisfying solution for treating it. Several blood cleansing approaches recently gained attention as promising interventions that target the main site of problem development-the blood. The focus of this study is an evaluation of the theoretical effectiveness of hemoadsorption therapy and pathogen reduction therapy. This is evaluated using the mathematical model of Murine sepsis, and the results of over 2,200 configurations of single and multiple intervention therapies simulated on 5,000 virtual subjects suggest the advantage of pathogen reduction over hemoadsorption therapy. However, a combination of two approaches is found to take advantage of their complementary effects and outperform either therapy alone. The conducted computational experiments provide unprecedented evidence that the combination of two therapies synergistically enhances the positive effects beyond the simple superposition of the benefits of two approaches. Such a characteristic could have a profound influence on the way sepsis treatment is conducted.
Figures
References
-
- Russel J. The current management of septic shock. Minerva Med. 99, 431–458 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. Focus on sepsis. Nat. Med. 18, 997 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Thiel S. W. et al. Early prediction of septic shock in hospitalized patients. J Hosp Med 5, 19–25 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Liu V. et al. Hospital deaths in patients with sepsis from 2 independent cohorts. J Am Med Assoc 312, 90–92 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

