EDGAR 2.0: an enhanced software platform for comparative gene content analyses
- PMID: 27098043
- PMCID: PMC4987874
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw255
EDGAR 2.0: an enhanced software platform for comparative gene content analyses
Abstract
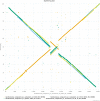
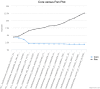
The rapidly increasing availability of microbial genome sequences has led to a growing demand for bioinformatics software tools that support the functional analysis based on the comparison of closely related genomes. By utilizing comparative approaches on gene level it is possible to gain insights into the core genes which represent the set of shared features for a set of organisms under study. Vice versa singleton genes can be identified to elucidate the specific properties of an individual genome. Since initial publication, the EDGAR platform has become one of the most established software tools in the field of comparative genomics. Over the last years, the software has been continuously improved and a large number of new analysis features have been added. For the new version, EDGAR 2.0, the gene orthology estimation approach was newly designed and completely re-implemented. Among other new features, EDGAR 2.0 provides extended phylogenetic analysis features like AAI (Average Amino Acid Identity) and ANI (Average Nucleotide Identity) matrices, genome set size statistics and modernized visualizations like interactive synteny plots or Venn diagrams. Thereby, the software supports a quick and user-friendly survey of evolutionary relationships between microbial genomes and simplifies the process of obtaining new biological insights into their differential gene content. All features are offered to the scientific community via a web-based and therefore platform-independent user interface, which allows easy browsing of precomputed datasets. The web server is accessible at http://edgar.computational.bio.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Tettelin H., Masignani V., Cieslewicz M., Donati C., Medini D., Ward N., Angiuoli S., Crabtree J., Jones A., Durkin A., et al. Genome analysis of multiple pathogenic isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae: implications for the microbial “pan-genome”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005;102:13950–13955. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Medini D., Donati C., Tettelin H., Masignani V., Rappuoli R. The microbial pan-genome. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005;15:589–594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

