Luteolin attenuates endotoxin-induced uveitis in Lewis rats
- PMID: 27098110
- PMCID: PMC5053922
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.16-0118
Luteolin attenuates endotoxin-induced uveitis in Lewis rats
Abstract
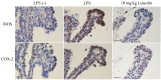
The aim of the present study was to investigate the efficacy of luteolin on endotoxin-induced uveitis (EIU) in rats. EIU was induced in Lewis rats by subcutaneous injections of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). One hr before the LPS injection, 0.1, 1 or 10 mg/kg luteolin or 1 mg/kg prednisolone was intraperitoneally injected. We investigated its effect upon clinical scores, cellular infiltration and protein leakage, as well as on the level of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin (PG) E2 in the aqueous humor (AqH). Histologic examination and immunohistochemical analysis in the iris-ciliary body (ICB) were performed to determine the expressions of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 and inducible NO synthase (iNOS), and then the activated nuclear factor (NF)-κB p65, I kappa B (IκB)-α degradation, phosphorylated (p)-IκB kinase (IKK) α/β and activator protein (AP)-1 c-Jun. Luteolin suppressed, in a dose-dependent manner, the clinical scores, number of inflammatory cells, the protein concentration, and the TNF-α, NO and PGE2 levels in the AqH and improved the histiologic status of the ocular tissue. Luteolin suppressed the expression of iNOS and COX-2 and the activated NF-κB p65, IκB-α degradation, p-IKKα/β and AP-1 p-c-Jun in the ICB. The anti-inflammatory potency of 10 mg/kg luteolin was as strong as that observed with 1 mg/kg prednisolone. These results demonstrate that luteolin attenuates ocular inflammation by inhibiting expression and release of inflammatory markers, along with the inhibition of the activated NF-κB pathway and at least partly AP-1 activity in the ICB.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Therapeutic anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin on endotoxin-induced uveitis in Lewis rats.J Vet Med Sci. 2016 Sep 1;78(8):1381-4. doi: 10.1292/jvms.16-0196. Epub 2016 May 7. J Vet Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27170432 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced ocular inflammation in rats via inhibition of nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation.J Vet Med Sci. 2016 Oct 1;78(9):1429-1438. doi: 10.1292/jvms.16-0166. Epub 2016 May 26. J Vet Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27238160 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of instillation of eyedrops containing disulfiram and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex on endotoxin-induced uveitis in rats.Curr Eye Res. 2012 Feb;37(2):124-31. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2011.622853. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Curr Eye Res. 2012. PMID: 22029776
-
Effects of blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.) extract on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo.Exp Eye Res. 2006 May;82(5):860-7. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2005.10.024. Epub 2005 Nov 23. Exp Eye Res. 2006. PMID: 16309673
-
Bioavailability and Pharmaco-therapeutic Potential of Luteolin in Overcoming Alzheimer's Disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019;18(5):352-365. doi: 10.2174/1871527318666190319141835. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30892166 Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering the pharmacological mechanism of the effects of the Banxia-Xiakucao Chinese Herb Pair on sleep disorder by a systems pharmacology approach.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 24;10(1):20454. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77431-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33235305 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of water-dispersible hesperetin on endotoxin-induced uveitis in rats involving the nuclear factor κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways.J Vet Med Sci. 2025 Feb 15;87(2):223-231. doi: 10.1292/jvms.24-0453. Epub 2025 Jan 16. J Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39814392 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin Attenuates APEC-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation via Inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB Signal Axis in the Ileum of Chicks.Animals (Basel). 2022 Dec 26;13(1):83. doi: 10.3390/ani13010083. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36611692 Free PMC article.
-
Autoimmune uveitis attenuated in diabetic mice through imbalance of Th1/Th17 differentiation via suppression of AP-1 signaling pathway in Th cells.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 3;15:1347018. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1347018. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38887289 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin on endotoxin-induced uveitis in Lewis rats.J Vet Med Sci. 2016 Sep 1;78(8):1381-4. doi: 10.1292/jvms.16-0196. Epub 2016 May 7. J Vet Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27170432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behar-Cohen F. F., Savoldelli M., Parel J. M., Goureau O., Thillaye-Goldenberg B., Courtois Y., Pouliquen Y., de Kozak Y.1998. Reduction of corneal edema in endotoxin-induced uveitis after application of L-NAME as nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in rats by iontophoresis. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 39: 897–904. - PubMed
-
- Brito B. E., O’Rourke L. M., Pan Y., Anglin J., Planck S. R., Rosenbaum J. T.1999. IL-1 and TNF receptor-deficient mice show decreased inflammation in an immune complex model of uveitis. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 40: 2583–2589. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

