Comparison of Vildagliptin and Pioglitazone in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled with Metformin
- PMID: 27098505
- PMCID: PMC4929227
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2016.40.3.230
Comparison of Vildagliptin and Pioglitazone in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled with Metformin
Abstract
Background: We compared the efficacies of vildagliptin (50 mg twice daily) relative to pioglitazone (15 mg once daily) as an add-on treatment to metformin for reducing glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods: The present study was a multicenter, randomized, active-controlled investigation comparing the effects of vildagliptin and pioglitazone in Korean patients receiving a stable dose of metformin but exhibiting inadequate glycemic control. Each patient underwent a 16-week treatment period with either vildagliptin or pioglitazone as an add-on treatment to metformin.
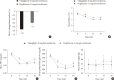
Results: The mean changes in HbA1c levels from baseline were -0.94% in the vildagliptin group and -0.6% in the pioglitazone group and the difference between the treatments was below the non-inferiority margin of 0.3%. The mean changes in postprandial plasma glucose (PPG) levels were -60.2 mg/dL in the vildagliptin group and -38.2 mg/dL in the pioglitazone group and these values significantly differed (P=0.040). There were significant decreases in the levels of total, low density lipoprotein, high density lipoprotein (HDL), and non-HDL cholesterol in the vildagliptin group but increases in the pioglitazone group. The mean change in body weight was -0.07 kg in the vildagliptin group and 0.69 kg in the pioglitazone group, which were also significantly different (P=0.002).
Conclusion: As an add-on to metformin, the efficacy of vildagliptin for the improvement of glycemic control is not inferior to that of pioglitazone in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes. In addition, add-on treatment with vildagliptin had beneficial effects on PPG levels, lipid profiles, and body weight compared to pioglitazone.
Keywords: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor; Metformin; Thiazolidinediones.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and tolerability of vildagliptin vs. pioglitazone when added to metformin: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind study.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008 Jan;10(1):82-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2007.00820.x. Epub 2007 Nov 22. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008. PMID: 18034842 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Vildagliptin or Pioglitazone on Glycemic Variability and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled with Metformin Monotherapy: A 16-Week, Randomised, Open Label, Pilot Study.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2017 Jun;32(2):241-247. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.241. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2017. PMID: 28685513 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of a Fixed-Dose Combination of Vildagliptin and Pioglitazone in Indian Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized, Open-Label, Comparative, Phase III Study.Cureus. 2023 Sep 1;15(9):e44548. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44548. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37795066 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of vildagliptin on glucose control over 24 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin.Diabetes Care. 2007 Apr;30(4):890-5. doi: 10.2337/dc06-1732. Epub 2007 Feb 2. Diabetes Care. 2007. PMID: 17277036 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of pioglitazone versus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a double-blind, randomized trial.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Dec;89(12):6068-76. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-030861. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 15579760 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Antihyperglycemic Agent Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association.Diabetes Metab J. 2017 Oct;41(5):337-348. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.5.337. Diabetes Metab J. 2017. PMID: 29086531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination Therapy of Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Metab J. 2017 Oct;41(5):357-366. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.5.357. Diabetes Metab J. 2017. PMID: 29086533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and efficacy of low dose pioglitazone compared with standard dose pioglitazone in type 2 diabetes with chronic kidney disease: A randomized controlled trial.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 31;13(10):e0206722. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206722. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30379936 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The rs12617336 and rs17574 Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Polymorphisms Are Associated With Hypoalphalipoproteinemia and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Serum Levels: A Case-Control Study of the Genetics of Atherosclerotic Disease (GEA) Cohort.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 11;12:592646. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.592646. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34178021 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy of oral hypoglycemic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Korean J Intern Med. 2017 Nov;32(6):974-983. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2017.354. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Korean J Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 29096431 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, Beagley J, Linnenkamp U, Shaw JE. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;103:137–149. - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. 6th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2013.
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:140–149. - PubMed
-
- Stumvoll M, Haring HU. Glitazones: clinical effects and molecular mechanisms. Ann Med. 2002;34:217–224. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

