Effects of Rebamipide on Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 27098506
- PMCID: PMC4929228
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2016.40.3.240
Effects of Rebamipide on Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Background: Gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms are common in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Rebamipide is an effective gastric cytoprotective agent, but there are few data on its usefulness in T2DM. The aim of this study is to evaluate the improvement of GI symptoms after rebamipide treatment in patients with T2DM.
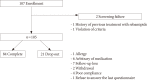
Methods: Patients with T2DM and atypical GI symptoms were enrolled. They took rebamipide (100 mg thrice daily) for 12 weeks and filled out the diabetes bowel symptom questionnaire (DBSQ) before and after rebamipide treatment. The DBSQ consisted of 10 questions assessing the severity of GI symptoms by a 1 to 6 scoring system. Changes in the DBSQ scores before and after rebamipide treatment were analyzed to evaluate any improvements of GI symptoms.
Results: A total of 107 patients were enrolled, and 84 patients completed the study. The mean age was 65.0±7.8, 26 patients were male (24.8%), the mean duration of T2DM was 14.71±9.12 years, and the mean glycosylated hemoglobin level was 6.97%±0.82%. The total DBSQ score was reduced significantly from 24.9±8.0 to 20.4±7.3 before and after rebamipide treatment (P<0.001). The DBSQ scores associated with reflux symptoms, indigestion, nausea or vomiting, abdominal bloating or distension, peptic ulcer, abdominal pain, and constipation were improved after rebamipide treatment (P<0.05). However, there were no significant changes in symptoms associated with irritable bowel syndrome, diarrhea, and anal incontinence. No severe adverse events were reported throughout the study.
Conclusion: Rebamipide treatment for 12 weeks improved atypical GI symptoms in patients with T2DM.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus, type 2; Gastrointestinal diseases; Rebamipide.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Letter: Effects of Rebamipide on Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2016;40:240-7).Diabetes Metab J. 2016 Aug;40(4):334-5. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2016.40.4.334. Diabetes Metab J. 2016. PMID: 27550210 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bytzer P, Talley NJ, Leemon M, Young LJ, Jones MP, Horowitz M. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus: a population-based survey of 15,000 adults. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:1989–1996. - PubMed
-
- Horowitz M, Dent J. Disordered gastric emptying: mechanical basis, assessment and treatment. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1991;5:371–407. - PubMed
-
- Rayner CK, Samsom M, Jones KL, Horowitz M. Relationships of upper gastrointestinal motor and sensory function with glycemic control. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:371–381. - PubMed
-
- Talley NJ, Young L, Bytzer P, Hammer J, Leemon M, Jones M, Horowitz M. Impact of chronic gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetes mellitus on health-related quality of life. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:71–76. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

